Haplotype representation
| Most 3' (first line) and most 5' (second line) limits of the extent of the insertion
(haplotype A)/deletion (haplotype B) Recombination breakpoint areas (rectangles, third line) |
 |
|
| Haplotype with insertion (L36092) | ||
| Haplotype A: | TRB |  |
|---|---|---|
| Haplotype with deletion (L36190) | ||
| Haplotype B: | TRB |  |
Extent of the insertion/deletion: 21 kb (21,659 bp)
- the extent of the insertion is 21kb (21,659 bp) in haplotype A compared to haplotype B.
- the extent of the deletion is 21kb (21,659 bp) in haplotype B compared to haplotype A.
The deletion in haplotype B probably results from an homologous recombination event which occurred between
the two duplicated regions of haplotype A (shown by rectangles, on the third line, and in yellow in the map).
The precise positions of the homologous recombination breakpoints cannot be determined inside these areas owing
to the high similarity between the duplicated sequences.
Genes are represented by the V-EXON
(L-PART1 not shown).
Haplotype description
A polymorphism by insertion/deletion of 3 genes between the TRBV4-2 and TRBV7-2 genes has been described in the human TRB locus [1,2]. It corresponds to haplotype A (21 kb insertion, L36092) and haplotype B (21 kb deletion, L36190). These haplotypes A and B correspond to the insertion/deletion of the pseudogene TRBV3-2, the functional TRBV4-3 gene and one gene belonging to the TRBV6 subgroup.
Arbitrarily as the two genes are highly homologous, the TRBV6-3 gene is described as the result of the duplication of the TRBV6-2 gene, and present in haplotype A (with insertion) or absent in haplotype B (with deletion). The 6kb duplicated and highly homologous regions encompassing the TRBV6-2 and TRBV6-3 genes in haplotype A and the TRBV6-2 gene in haplotype B are shown in yellow.
If haplotype B indeed results from a deletion which occurred after the TRBV6-2 gene duplication, the recombination can have occurred at any homologous position of the 6kb duplicated regions, either upstream or downstream of the V-EXON, or within the V-EXON. Assignment of the gene name TRBV6-2 to the TRBV6 subgroup gene in haplotype B follows the rules of the nomenclature based on positions in the locus [3,4]. It does not mean that the recombination occurred necessarily downstream of the TRBV6-2 gene.
TRBV gene positions
| IMGT/LIGM-DB accession numbers |
IMGT Gene name | Positions of the V-EXON | V-EXON length (bp) |
Distance between the V-EXONs (bp) |
| L36092 |
TRBV4-2 TRBV6-2 TRBV3-2 TRBV4-3 TRBV6-3 TRBV7-2 |
138078..138531 141898..142330 151879..152044 155338..155791 163579..164011 167212..167708 |
453 433 165 453 433 496 |
3367 9549 3294 7788 3201 |
| L36190 |
TRBV4-2 TRBV6-2 TRBV7-2 |
1725..2178 5412..5843 9043..9525 |
453 431 482 |
3234 3200 |
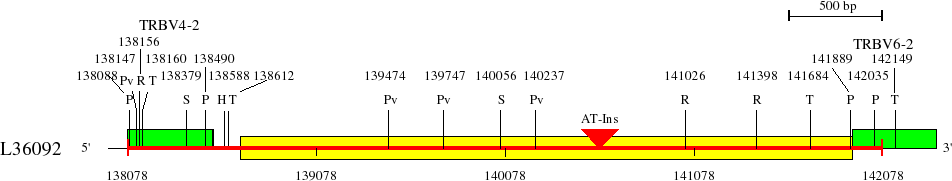
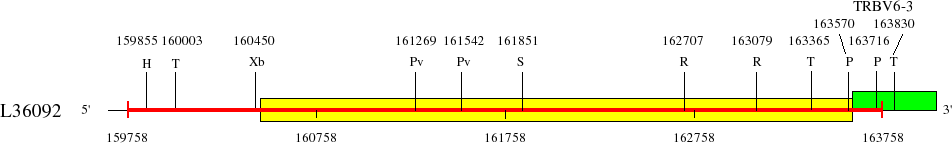
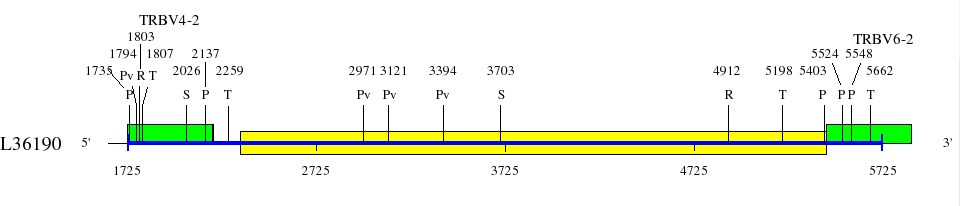
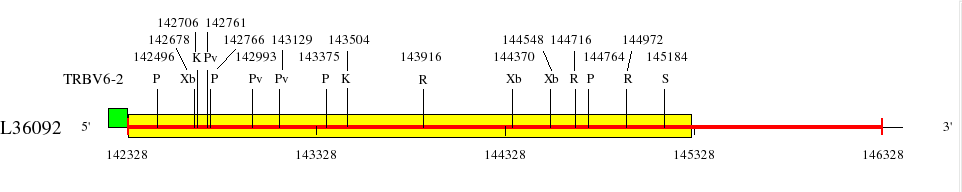
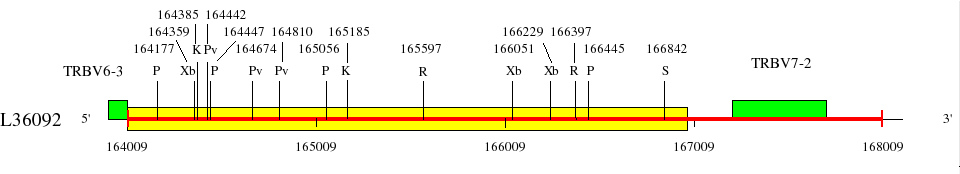
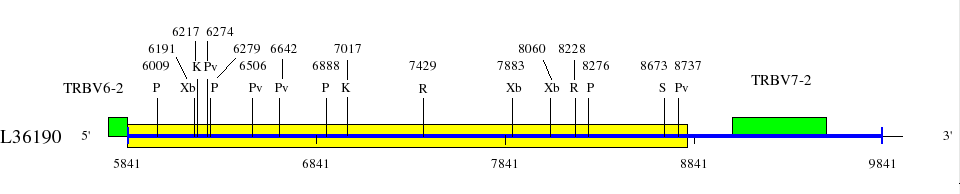
Restriction sites in L36092 (red) and L36190 (blue)
Upstream of TRBV6-2 (138078..142330)
Upstream of TRBV6-3 (159758..164011)
Upstream of TRBV6-2 (1725..5843)
Downstream of TRBV6-2 (142328..145528)
Downstream of TRBV6-3 (164009..167214)
Downstream of TRBV6-2 (5841..9045)
Legend:
AT-Ins: Insertion of a region rich in AT from 140525 to 140664 in L36092 (length 139 bp).
B:
BamHI
G∧GATCC
R:
EcoRI
G∧AATTC
H:
HindIII
A∧AGCTT
K:
KpnI
GGTAC∧C
P:
PstI
CTGCA∧G
S: SacI (SstI) GAGCT∧C
T: TaqI T∧CGA
Xb: XbaI T∧CTAGA
X: XhoI C∧TCGAG
Genes are represented by the V-EXON (in green) (L-PART1 not shown). TRBV6-2 and TRBV6-3 V-EXON are split on two lines.
Numbers above the restriction sites indicate the position of the nucleotide preceding the enzyme cuts in the restriction enzyme sites (for example position of G in an EcoRI site). No BamHI and XhoI sites were found in the areas shown in the maps.
Numbers below the map indicate positions in L36092 and L36190. L36092 is only available in IMGT/LIGM-DB (Germline gene table: Human TRBV).
| [1] | Zhao, T.M. et al., J. Exp. Med., 180, 1405-1414 (1994) PMID: 7931073 |
| [2] | Rowen, L. et al., Science, 272, 1755-1762 (1996) PMID: 8650574 |
| [3] | Lefranc, M.-P., Nomenclature of the human T cell receptor genes, Current Protocols in Immunology, A.1O.1-A.1O.23 (2000). |
| [4] | Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G., The T cell receptor FactsBook, Academic Press, London, 398 pages (2001) ISBN:0124413528. |



