Mammalian cell lines used in antibody engineering and expression system
1. Mammalian cell lines
1.1. Mouse myeloma and hybridoma cell lines derived from MOPC21 and used as fusion partners
Among the cell lines derived from MOPC21, the SP2/0 (hybridoma), P3-X63-Ag8.653 (myeloma) and NS0 (myeloma) cell lines are frequently used as fusion partners in the generation of hybridomas. The table below shows their clone origin and their characteristics.
| Cell line name | Other cell line names | Species and strain | Cell type and cell lineage | Clone origin | IG production | Cell line characteristics | ECACC | ATCC | IMGT references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOPC21 | MOPC 21, MOPC21 (mineral oil induced plasmacytoma number 21) | Mus musculus BALB/c (inbred female mouse) | myeloma, B cell | secreting IgG1-kappa (H+L+) | Horibata and Harris 1970 [1] | ||||
| P3K | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | derived from MOPC21 | secreting IgG1-kappa (H+L+) | suspension, heterogeneous population | Horibata and Harris 1970 [1] | |||
| P3-X27 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from P3K | secreting IgG1-kappa (H+L+) | Ramasamy et al. 1974 [2] | ||||
| NSI/1 | 289-16 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from P3-X27 | non secreting, synthesing kappa (H-L+ intracellular) | suspension | Ramasamy et al. 1974 [2], Cowan et al. 1974 [7] | ||
| NS-1 | P3/NSI/1-Ag4-1, NS-1-Ag4-1, P3-NS-1/1-Ag4-1 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from NSI/1 | non secreting, synthesing kappa (H-L+ intracellular) | suspension, resistant to 8-azaguanine | 85011427 | TIB-18™ | Köhler et al. 1976 [8] |
| NS0 | NS/0, NS0/1 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from NS-1 | non-IG secreting, non-IG synthetising (H-L-) | suspension, resistant to 8-azaguanine | 85110503 | Galfrè and Milstein 1981 [9] | |
| P3-X63 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from P3X27 | secreting IgG1-kappa (H+L+) | Ramasamy et al. 1974 [2] | ||||
| P3-X63-Ag8 | P3X63Ag8, P3/X63Ag8, X63 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from P3X27 | secreting IgG1-kappa (H+L+) | suspension, resistant to 8-azaguanine | 85011401 | TIB-9™ | Köhler et Milstein 1975 [3] |
| P3-X63-Ag8-U1 | P3X63Ag8U.1, P3X63Ag8U1, P3U1 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | variant of P3-X63-Ag8.653 | non-IG secreting, synthesing kappa (H-L+) | suspension | 94120802 | CRL-1597™ | Yelton D.E. et al. 1979 [5] |
| P3-X63-Ag8.653 | P3X63Ag8.653, P3/X63Ag8.653, X63-Ag8.653, X63Ag8.653, X63.653, Ag8 | Mus musculus BALB/c | myeloma, B cell | cloned from P3-X63-Ag8 | non-IG secreting, non-IG synthetising (H-L-) | suspension | 85011420 | CRL-1580™ | Kearney J.F. et al. 1979 [6] |
| Sp2/0 | Sp2/0-Ag-14, Sp2/0-Ag14, SP-2 | Mus musculus BALB/c | hybridoma, B cell | obtained by fusion with P3X63Ag8 | non-IG secreting, non-IG synthetising (H-L-) | suspension, resistant to 8-azaguanine | 85072401 | CRL-1581™ CRL-8287™ | Shulman M. et al. 1978 [4] |
| YB2/0 | YB2/3HL.P2.G11.16Ag.20 | Rattus norvegicus | hybridoma, B lymphoblast | obtained by fusion with Y3/Ag1.2.3 | non-IG secreting | suspension, resistant to 8-azaguanine | CRL-1662™ | Kilmartin JV, et al. 1982 [10] |
YB2/0 was obtained by fusing Y3/Ag1.2.3 (ATCC CRL-1631) cells with spleen cells from an AO strain rat. YB2/0 can be used as a fusion partner for rat B cells to make rat - rat hybridomas.
1.2. Rat hybridoma cell line used as fusion partner
| Cell line | Other cell line names | Species and strain | Cell type and cell lineage | Clone origin | IG production | Cell line characteristics | ECACC | ATCC | IMGT references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YB2/0 | YB2/3HL.P2.G11.16Ag.20 | Rattus norvegicus | hybridoma, B lymphoblast | obtained by fusion with Y3/Ag1.2.3 | non-IG secreting | suspension, resistant to 8-azaguanine | CRL-1662™ | Kilmartin JV, et al. 1982 [10] |
The cell lines used as fusion partners do not grow in HAT medium (they die in the presence of HAT, they are HAT or HAz-sensitive). They lack a functional HGPRT, i.e., they are resistant to 8-azaguanine (the Ag in the cell names stands azaguanine).
Cholesterol requirements
NS-1, P3-X63-Ag8, P3-X63-Ag.653 are cholesterol auxotrophs (requires cholesterol). In contrast, hybridoma Sp2/0 do not require neither LDL nor cholesterol (the fusion partner bringing the necessary genes) [11].
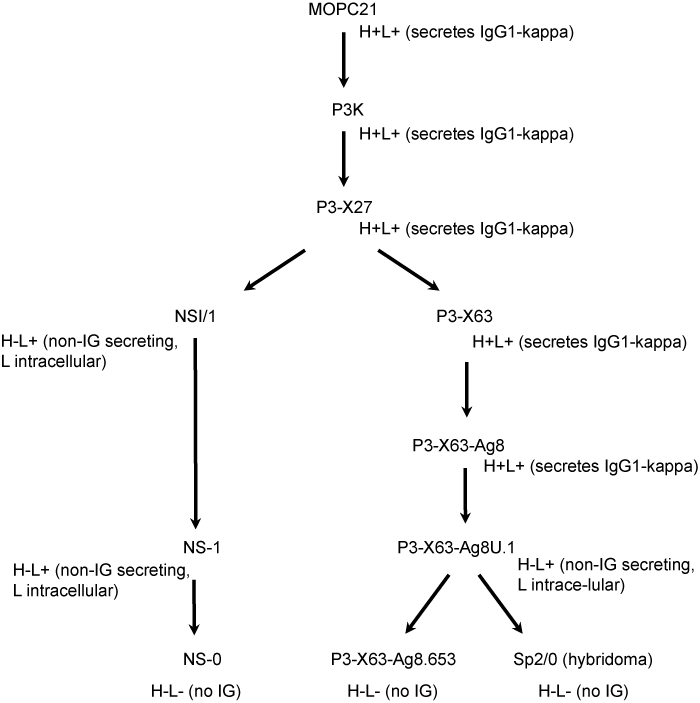
Figure 1. Myeloma cell lines derived from MOPC21 showing SP2/0 (hybridoma), P3-X63-Ag8.653 (myeloma) and NS0 (myeloma) used as fusion partners in the generation of hybridomas.
The original hybridoma Sp2/3-3 was obtained by fusion of BALB/c spleen cells producing an anti-SRBC mAb Sp2 (from mouse immunized with sheep RBC) with the P3-X63-Ag8 (X63) myeloma [3].
1.3. Hamster cell lines used as protein expression system
| Cell line | Other cell line names | Species and strain | Cell type and cell lineage | Clone origin | IG production | Cell line characteristics | ECACC | ATCC | Companies | IMGT references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHO | CHO-ori, Chinese Hamster Ovary | Cricetulus griseus | epithelial | adherent | 85050302 | Puck TT et al. 1958 [12] | ||||
| FreeStyle™ CHO-S Cells | CHO-derived suspension culture | Cricetulus griseus | derived from CHO-S | suspension | Life Technologies:R800-07 | |||||
| CHO-K1 | CHOK1, CHO K1, CHO cell clone K1 | Cricetulus griseus | epithelial | derived from CHO | adherent | 85051005 | CCL-61™ | Kao FT and Puck TT 1968 [13] | ||
| POTELLIGENT® CHOK1SV | CHO-K1SV, suspension variant of CHO-K1 | Cricetulus griseus | derived from CHO-K1 | suspension | Lonza | |||||
| CHO/dhFr- | Cricetulus griseus | epithelial | adherent, dhFr- | 94060607 | ||||||
| CHO-DUK-B11 | CHO duk-, DXB11, CHO-DUKX | Cricetulus griseus | epithelial | derived from CHO-K1 | adherent, dhFr- | CRL-9096™ | Urlaub G et al. 1980 [14] | |||
| CHO-DG44 Cells (cGMP banked) | CHO DG44 | Cricetulus griseus | derived from CHO-K1 | suspension, dhFr- | Life Technologies:A11000-01 | Urlaub G et al. 1983 [15] |
1.4. Human cell lines
HEK293 cell line derived from human embryonic kidney cells transformed with sheared fragments of adenovirus type 5 DNA has been widely used in the production of monoclonal antibody. Some derivatives were further transformed either with the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen, termed HEK293T, or with the Epstein Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1), termed HEK293E, using an origin of replication (ori) of SV40 or EBV, respectively.PER.C6® cell lines are derived from human embryonic retina cells that have been immortalized by transfecting the E1 genes from adenovirus 5 DNA.19. PER.C6® cells can proliferate indefinitely in suspension under serum-free conditions.
2. Selection
2.1. HAT
Hybridoma cells are selected using HAT (Hypoxanthine Aminopterin Thymidine) medium.HAT selection depends on the fact that mammalian cells can synthesize nucleotides by two different pathways: the de novo and the salvage pathways. Aminopterin (a folic acid analog) blocks the de novo pathway, while hypoxanthine and thymidine allow growth via the salvage pathway.
Indeed, the DNA de novo synthesis (in which a methyl or formyl group is transferred from an activated from of tetrahydrofolate) is blocked by Aminopterin. When the de novo pathway is blocked, cells utilize the salvage pathway, which bypasses the aminopterin block by converting purines and pyrimidines directly into DNA. The enzymes catalyzing the salvage pathway include hypoxanthine-guanine phosphorribosyl transferase (HGPRT) and thymidine kinase (TK). This pathway can convert hypoxanthine in IMP, a reaction catalysed by HGPRT. It can also convert thymidine in dTMP, a reaction catalysed by TK.
On this medium, only cells which have functional HGPRT and TK will grow via the salvage pathway.
Figure: Principle of HAT selection (origin: http://nfs.unipv.it/nfs/minf/dispense/immunology/lectures/files/monoclonal_antibodies.html)
| [1] | Horibata K. and Harris A.W. Exp Cell Res. 60(1):61-77 (1970) PMID: 5439579 |
| [2] | Ramasamy R. et al. Nature. 249(457):573-4 (1974) PMID: 4545851 |
| [3] | Köhler G. and Milstein C. Nature. 256(5517):495-7 (1975) PMID: 1172191 |
| [4] | Shulman M. et al. Nature. 276(5685):269-70 (1978) PMID: 714156 |
| [5] | Yelton D.E. et al. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 81:1-7 (1978) PMID: 567551 |
| [6] | Kearney J.F. et al. J Immunol. 123(4):1548-50 (1979) PMID: 113458 |
| [7] | Cowan N.J.et al. J Mol Biol. 90(4):691-701 (1974) PMID: 4449137 |
| [8] | Köhler G. et al. Eur J Immunol. 6(4):292-5 (1976) PMID: 825374 |
| [9] | Galfrè G. and Milstein C. Methods Enzymol. 73(Pt B):3-46 (1981) PMID: 730068 |
| [10] | Kilmartin J.V. et al. J Cell Biol. 93(3):576-82 (1982) PMID: 6811596 |
| [11] | Sato J.D. et al. J Exp Med. 165(6):1761-6 (1987) PMID: 3585251 |
| [12] | Puck T.T. et al. J Exp Med. 108(6):945-56 (1958) PMID: 13598821 |
| [13] | Kao FT and Puck TT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 60(4):1275-81 (1968) PMID: 5244736 |
| [14] | Urlaub G. et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 77(7):4216-20 (1980) PMID: 6933469 |
| [15] | Urlaub G. et al. Cell. 33(2):405-12 (1983) PMID: 6305508 | [16] | Bradbury A.R.M. et al. MAbs. 10(4):539-546 (2018) PMID: 29485921 |
Last updated: Friday, 06-Feb-2026 15:23:16 CET
Authors: Karima Cherouali, Mélissa Cambon, Souphatta Sasorith and Marie-Paule Lefranc
IMGT Home page |
IMGT Repertoire (IG and TR) |
IMGT Repertoire (MH) |
IMGT Repertoire (RPI) |
IMGT Index |
IMGT Scientific chart |
IMGT Education |
IMGT Latest news ![]()



© Copyright 1995-2026 IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system® | Terms of use | About us | Contact us | Citing IMGT

