Here you are: IMGT Web resources > IMGT Education
Amino acids
Formula of the 20 common amino acids and structural details of the side chains
Formula of the 20 common amino acids
The formula of an amino acid comprises, bound to a carbon (alpha carbon):
- a carboxyl group -COOH
- an amine group -NH2
- an atom of hydrogen -H
- a variable radical -R, that is the functional group (in red in the table) of the amino acid.
Chemically speaking, an amino acid is a carboxylic acid which has an amine group attached to it. The general linear formula of an amino acid is R-CH(NH2)-COOH.
The 20 common amino acids are grouped in classes according to their side chains:
Click here for IMGT classes of the 20 common amino acids 'Physicochemical' properties.
Structural formula
Amino acids with uncharged side chains
| POLAR SIDE CHAINS | NON POLAR SIDE CHAINS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SERINE | 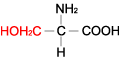 |
GLYCINE | 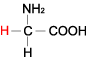 |
| THREONINE | 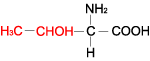
| ALANINE | 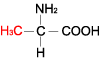 |
| TYROSINE | 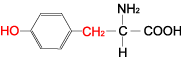 |
CYSTEINE (1) | 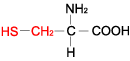 |
| ASPARAGINE | 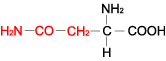 |
VALINE | 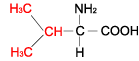 |
| GLUTAMINE | 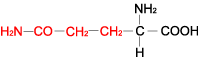 |
LEUCINE | 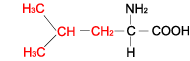 |
| ISOLEUCINE | 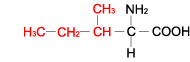 | ||
| PROLINE | 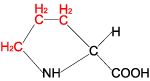 | ||
| METHIONINE | 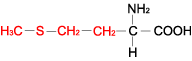 | ||
| PHENYLALANINE | 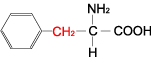 | ||
| TRYPTOPHAN | 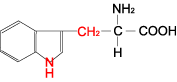 | ||
Amino acids with charged side chains
Charged side chains are POLAR.
| ACIDIC SIDE CHAINS | BASIC SIDE CHAINS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASPARTIC ACID |
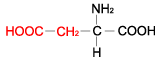 |
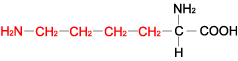
LYSINE |
 |
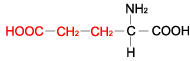
| GLUTAMIC ACID |
 |
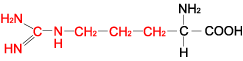
ARGININE |
 |
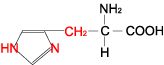
| HISTIDINE |
 |
||
- (1) Paired cysteines allow disulfide bonds to form in proteins: -CH2-S-S-CH2-
Molecular and linear formulas
| Amino acid | Abbreviations | Molecular formula | Linear formula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | Ala | A | C3H7NO2 | CH3-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Arginine | Arg | R | C6H14N4O2 | HN=C(NH2)-NH-(CH2)3-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Asparagine | Asn | N | C4H8N2O3 | H2N-CO-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D | C4H7NO4 | HOOC-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Cysteine | Cys | C | C3H7NO2S | HS-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q | C5H10N2O3 | H2N-CO-(CH2)2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E | C5H9NO4 | HOOC-(CH2)2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Glycine | Gly | G | C2H5NO2 | NH2-CH2-COOH |
| Histidine | His | H | C6H9N3O2 | NH-CH=N-CH=C-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I | C6H13NO2 | CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Leucine | Leu | L | C6H13NO2 | (CH3)2-CH-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Lysine | Lys | K | C6H14N2O2 | H2N-(CH2)4-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Methionine | Met | M | C5H11NO2S | CH3-S-(CH2)2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F | C9H11NO2 | Ph-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Proline | Pro | P | C5H9NO2 | NH-(CH2)3-CH-COOH |
| Serine | Ser | S | C3H7NO3 | HO-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Threonine | Thr | T | C4H9NO3 | CH3-CH(OH)-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W | C11H12N2O2 | Ph-NH-CH=C-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y | C9H11NO3 | HO-Ph-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Valine | Val | V | C5H11NO2 | (CH3)2-CH-CH(NH2)-COOH |
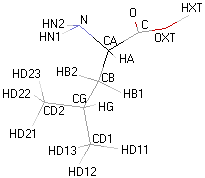
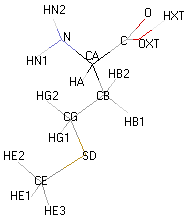
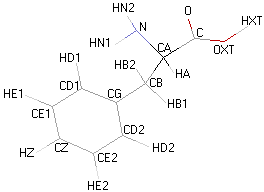
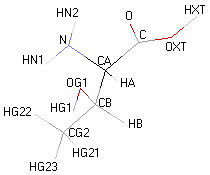
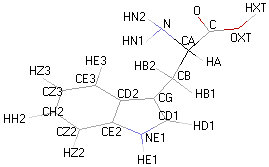
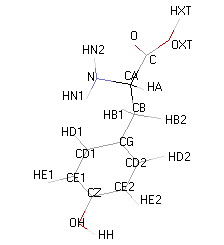
Structural details of the side chains: formula, 3D model and atoms nomenclature
The general formula of an amino acid is composed by a carbon alpha atom, a carboxyl group, a side chain group and an amino group.
- Molecular formula: structural formula with the carbon alpha atom and the radical of each amino acid.
- 3D molecular model: a ball and stick model of the amino acids is shown. Oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur atoms are represented by colored spheres (Oxygen: red, Hydrogen: white, Nitrogen: blue, Sulfur: yellow). The carbon alpha atom is represented by black sticks and other carbons by grey sticks.
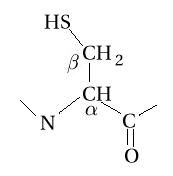
- Atoms nomenclature:
- CA : Carbon alpha
- HB : Hydrogen of carbon beta
- HN : Hydrogen of nitrogen
- OXT : Oxygen of hydroxyl
- HXT : Hydrogen of hydroxyl
-
Representation of an
amino acid example (cystein) engaged in a peptide chain and showing the carbone
alpha and the carbone beta.
| AMINO ACID | MOLECULAR FORMULA | 3D MOLECULAR MODEL | ATOMS NOMENCLATURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALANINE | 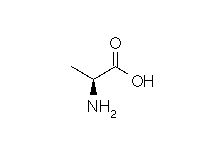 |
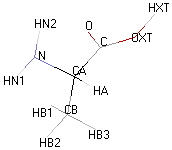 |
|
| ARGININE | 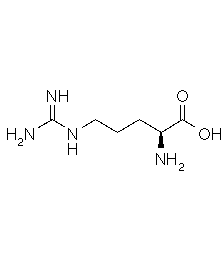 |
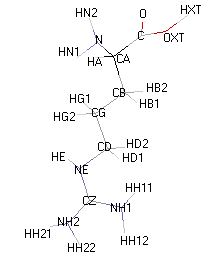 |
|
| ASPARAGINE | 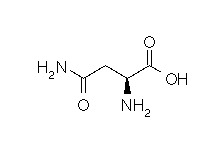 |
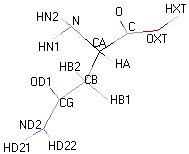 |
|
| ASPARTIC ACID | 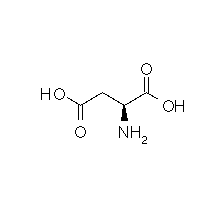 |
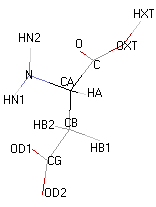 |
|
| CYSTEINE | 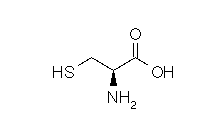 |
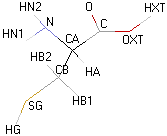 |
|
| GLUTAMINE | 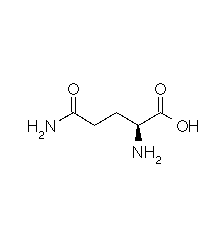 |
||
| GLUTAMIC ACID | 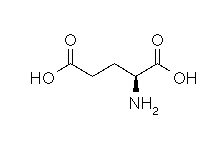 |
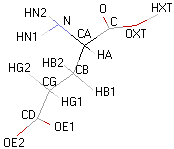 |
|
| GLYCINE | 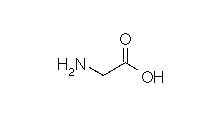 |
||
| HISTIDINE | 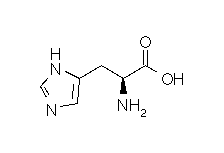 |
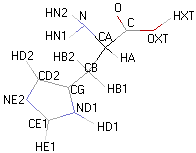 |
|
| ISOLEUCINE | 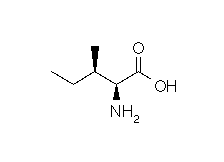 |
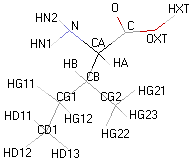 |
|
| LEUCINE | 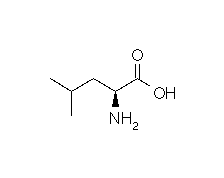 |
 |
|
| LYSINE | 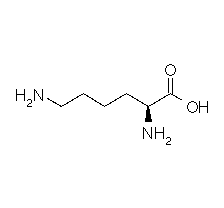 |
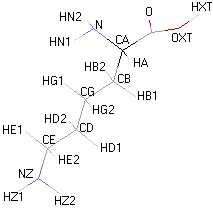 |
|
| METHIONINE | 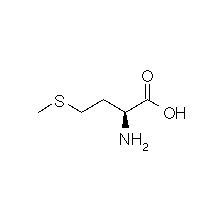 |
 |
|
| PHENYLALANINE | 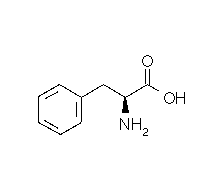 |
 |
|
| PROLINE | 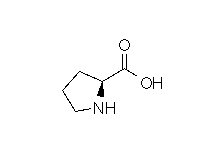 |
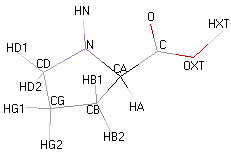 |
|
| SERINE | 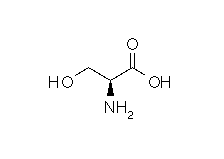 |
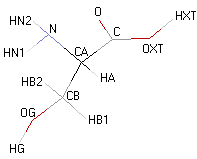 |
|
| THREONINE | 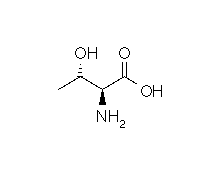 |
 |
|
| TRYPTOPHAN | 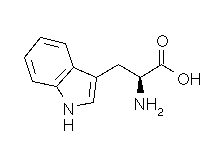 |
 |
|
| TYROSINE | 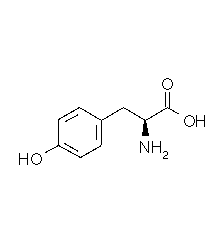 |
 |
|
| VALINE | 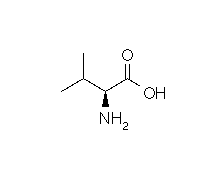 |
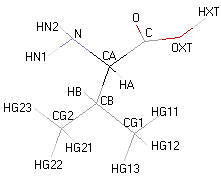 |




