Citing this page: Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G. Human Gm, Km and Am allotypes and their molecular characterization: a remarkable demonstration of polymorphism In: B. Tait, F. Christiansen (Eds.), Immunogenetics, chap. 34, Humana Press, Springer, New York, USA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012; 882, 635-680. PMID: 22665258
Km allotypes
- Km allotype characterization
- Km phenotypes and Km genotypes
- Km phenotypes in Lebanese and Tunisian populations (LIGM data)
- Km allele frequencies in Lebanese and Tunisian populations (LIGM data)
- Km allele frequency overview
- Correspondence between Km alleles and IGKC allele names
- Description of mutations for the Km alleles
- Km3, Km1,2 and Km1 allotypes on IGKC three-dimensional structure
Allotypes have been identified for the human IGKC gene and are designated as Km (for 'kappa marker') (previously Inv) [1-2].
Km allotype characterization
Km allotypes are determined by the hemagglutination technique inhibition [3-4]. There are three identified Km allotypes: Km1, Km2 and Km3. They correspond to IGKC amino acid changes at position 45.1 and 101, according to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN (Table).
Km phenotypes and Km genotypes
Given the rarity of anti-Km2 and anti-Km3 reagent antibodies, only the Km1 allotype is tested in most of the population studies. In the table below are shown:
- the six Km genotypes defined by their Km alleles,
- the five Km phenotypes observed when sera are tested for the three allotypes Km1, Km2 and Km3,
- the three Km phenotypes observed when sera are only tested for allotypes Km1 and Km2,
- the two Km phenotypes observed when sera are only tested for allotype Km1.
| Km genotypes a | Km phenotypes b | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sera tested for allotypes Km1,Km2 and Km3 |
Sera only tested for allotypes Km1 and Km2 |
Sera only tested for allotype Km1 |
|
| Km1/Km1 | Km1 | Km1,-2 | Km1 |
| Km1/Km3 | Km1,3 | ||
| Km1/Km1,2 or Km1,2/Km1,2 |
Km1,2 | Km1,2 | |
| Km1,2/Km3 | Km1,2,3 | ||
| Km3/Km3 | Km3 | Km-1,-2 | Km-1 |
a Km alleles and genotypes were previously written underlined and using superscript
(for example Km1/Km1).
b Numbers of the Km allotypes and phenotypes are written between parentheses.
Km phenotypes in Lebanese and Tunisian populations (LIGM data)
| Km phenotypes | Lebaneses [4] (1) | Tunisians [5] | Tunisian Berbers [6] (2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahdia (2) | Sfax (1) | Kesra | Takrouna-Jeradou | Douiret-Chenini | |||
| Km1 | Km1,-2 | 33 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Km1,3 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Km1,2 | Km1,2 | 421 | 7 | 37 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Km1,2,3 | 59 | 19 | 36 | 32 | |||
| Km3 | Km-1,-2 | 2584 | 163 | 101 | 60 | 85 | 69 |
| Total number of individuals | 3038 | 236 | 142 | 80 | 123 | 107 | |
Km allele frequencies in Lebanese and Tunisian populations (LIGM data)
| Km allele frequencies | Lebanon [4] (1) | Lebaneses [7] (1) | Tunisians [5] (3) | Tunisian Berbers [6] (2) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunnites | Shiites | Druzes | Maronites | Orthodox Greeks | Catholic Greeks | Armenians | Mahdia (2) | Sfax (1) | Kesra | Takrouna-Jeradou | Douiret-Chenini | ||
| Km3 | 0.922 | 0.907 | 0.917 | 0.941 | 0.923 | 0.930 | 0.917 | 0.933 | 0.833 | 0.842 | 0.879 | 0.826 | 0.795 |
| Km1,2 | 0.072 | 0.079 | 0.079 | 0.057 | 0.074 | 0.066 | 0.074 | 0.061 | 0.149 | 0.144 | 0.120 | 0.173 | 0.204 |
| Km1 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Total number of alleles | 6076 | 552 | 644 | 472 | 1596 | 726 | 564 | 660 | 472 | 284 | 160 | 246 | 214 |
Km allele frequency overview
| Km allele frequencies | Caucasoids [9-18] | Mongoloids and Negroids [12,16,19-21] | Indians of South America [22-24] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Km3 | 0.9 | 0.8-0.5 | 0.4 |
| Km1,2 | 0.08 | 0.2-0.5 | 0.5-0.6 |
| Km1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
Correspondence between Km alleles and IGKC allele names
| Km alleles | IGKC allele names | Amino acid positions (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45.1 | 101 | ||
| (46) | (84) | ||
| 153 | 191 | ||
| Km3 | IGKC*01 IGKC*02 IGKC*03 IGKC*05 |
Ala GCC |
Val GTC |
| Km1,2 | IGKC*04 | Ala GCC |
Leu CTC |
| Km1 | IGKC*06 (5) | Val (GTC) |
Leu (CTC) |
Description of mutations for the Km alleles
Description of mutations for the Km alleles is according to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN. Between parentheses are shown the expected mutations responsible for the Km1 amino acid changes.
| Km alleles | Description of mutations |
|---|---|
| Km3 | c134.1 ,A45.1 | g301 ,V101 | |
| Km1,2 | c134.1 ,A45.1 | g301>c ,V101>L| |
| Km1 | (c134.1>t),A45.1>V|(g301>c),V101>L| |
Km3, Km1,2 and Km1 allotypes on IGKC three-dimensional structure
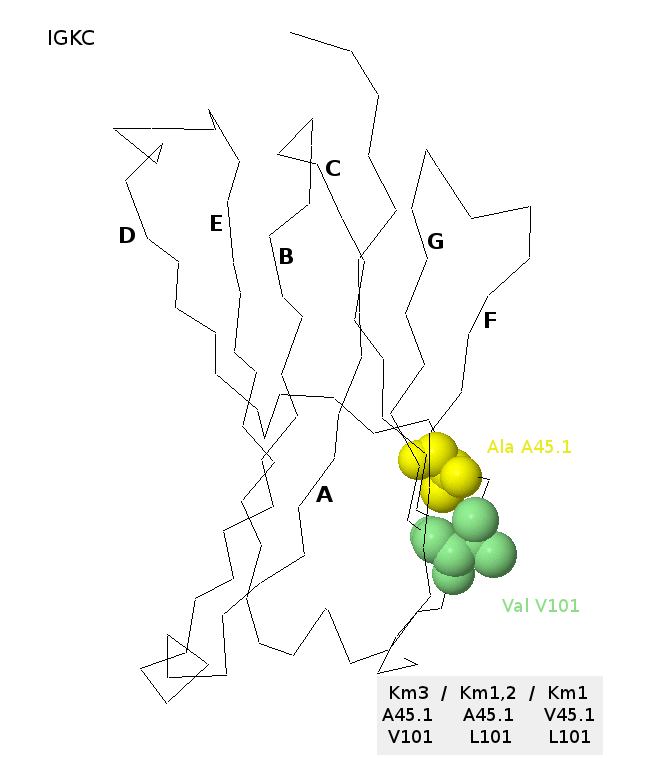
The C-KAPPA domain (encoded by IGKC*01) is from the b12 antibody (IMGT/3Dstructure-DB, code PDB:1hzh). The alanine Ala A45.1 (strand CD) and the valine Val V101 (strand F) are shown [32]. The A45.1 and V101 corresponds to the Km3 allotype. The A45.1 and L101 would correspond to Km1,2, and the V45.1 and L101 would correspond to Km1 [32].
| Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G. Human Gm, Km and Am allotypes and their molecular characterization: a remarkable demonstration of polymorphism In: B. Tait, F. Christiansen (Eds.), Immunogenetics, chap. 34, Humana Press, Springer, New York, USA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012; 882, 635-680. PMID: 22665258 LIGM: 406 |
| (1) | Sera only tested for Km1 and Km2 allotypes. The Km1 and Km1,2 allele frequencies were calculated, and the Km3 allele frequency was deduced by difference. |
| (2) | Sera tested for Km1, Km2 and Km3 allotypes. |
| (3) | Another study on the same Tunisian populations provided similar frequencies [8]. |
| (4) | Amino acid positions according to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN [30] (in bold), to the IMGT exon numbering (between parentheses) and to the Kabat numbering (in italics). Characterization of amino acids for Km allotypes are from [25-29]. |
| (5) | Not sequenced at the nucleotide level. Expected codons are shown between parentheses (G. Lefranc and M.-P. Lefranc, 13/05/2003) [31]. |
| [1] | Ropartz, C. et al., Nature, 189, 586-587 (1961). |
| [2] | Steinberg, A.G. et al., Vox Sang., 7, 151-156 (1962). |
| [3] | Lefranc, G., Allotypes et haplotypes des immunoglobulines dans les communautés libanaises :
intérêt exceptionnel en immunogénétique et séro-anthropologie.
Thèse de Doctorat d'Etat es Sciences Naturelles. Faculté des Sciences, Université de Rouen, 21 mars 1978. |
| [4] | Lefranc, G. et al., Acta Anthropogenetica, 1, 34-45 (1976) LIGM:3.
|
| [5] | Lefranc, G. et al., Hum. Genet., 50, 199-211 (1979) PMID: 511135 LIGM:9. |
| [6] | Chaabani, H. et al., J.Immunogenet., 11, 107-113 (1984) PMID: 6427354 LIGM:25. |
| [7] | Lalouel, J.M. et al., Acta Anthropogenetica, 1, 15-33 (1976) LIGM:2. |
| [8] | Helal, A.N. et al., Exp. Clin. Immunogenet. 5, 1-14 (1988) PMID: 3155402 LIGM:55. |
| [9] | Ropartz, C. et al., Acta Genet. (Basel). 13, 109-123 (1963). |
| [10] | Ropartz, C. et al., Bull. Soc. Anthrop, Paris, 4, XIe ser., 458-469 (1963). |
| [11] | Steinberg A.G., In Symposium on Immunogenetics. J.B. Lippincott Co. ed. Philadelphia (1966). |
| [12] | Steinberg A.G. et al., Annu. Rev. Genet., 3, 25-52 (1969). |
| [13] | Ropartz, C. et al., Hum. Hered. 20, 275-280 (1970) PMID: 4099120. |
| [14] | Ropartz, C. et al., Hum. Hered. 20, 456- (1970). |
| [15] | Ropartz, C. et al., Hum. Hered. 22, 508-518 (1972) PMID: 4206588. |
| [16] | Steinberg, A.G. et al., Isr. J. Med. Sci., 9, 1249-1256 (1973) PMID: 4775108. |
| [17] | Schanfield, M.S. et al., Hum. Hered., 25, 370-377 (1975) PMID: 1222944. |
| [18] | Schanfield, M.S. et al., Hum. Hered., 25, 382-392 (1975) PMID: 1222946. |
| [19] | Steinberg, A.G. and Matsumoto, H., Hum. Biol., 36, 77-85 (1964). |
| [20] | Loghen E.van et al., Ann. Hum. Genet., 33, 351-359 (1970). |
| [21] | Jenkins, T. et al., Am. J . Phys. Anthrop., 32, 197-218 (1970) PMID: 4191313. |
| [22] | Daveau, M. et al., Hum. Hered., 25, 88-92 (1975) PMID: 1150304. |
| [23] | Salzano, F.M. and Steinberg, A.G., Am. J. Hum. Genet., 17, 273-279 (1965). |
| [24] | Salzano, F.M. et al., A.G., Am. J. Hum. Genet., 25, 167-177 (1973) PMID: 4120238. |
| [25] | Baglioni, C. et al., Science, 152, 1517-1519 (1966) PMID: 5934342. |
| [26] | Hilschmann, N. and Craig, L.C., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 53, 1403-1409 (1965) PMID: 5324619. |
| [27] | Milstein C., Nature, 209, 370-372 (1966) PMID: 5920238. |
| [28] | Milstein, C.P. et al., Nature, 248, 160-161 (1974) PMID: 4132042. |
| [29] | Steinberg, A.G. et al., Immunogenetics, 2, 1-10 (1974). |
| [30] | Lefranc, M.-P. et al., Dev. Comp. Immunol., 29, 185-203 (2005). |
| [31] | Lefranc G. and Lefranc M.-P. The Immunoglobulin FactsBook, Academic press, London, UK, 458 pages (2001). |
| [32] | Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G., Methods Mol. Biol. 882, 635-680 (2012). PMID: 22665258 LIGM: 406 |



