IMGT Repertoire (IG and TR)
Locus representation: human (Homo sapiens) IGL locus on chromosome 22 (22q11.2)
Lefranc, M.-P., Exp. Clin. Immunogenet., 18, 242-254 (2001). PMID: 11872955
Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G., The Immunoglobulin FactsBook, Academic Press, London, 458 pages (2001).
Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G., In: Molecular Biology of B cells, pp 37-59 (2004).
Human (Homo sapiens) IGL locus on chromosome 22 (22q11.2)
The orientation of the human (Homo sapiens) IGL locus on chromosome 22 (22q11.2) is forward (FWD).
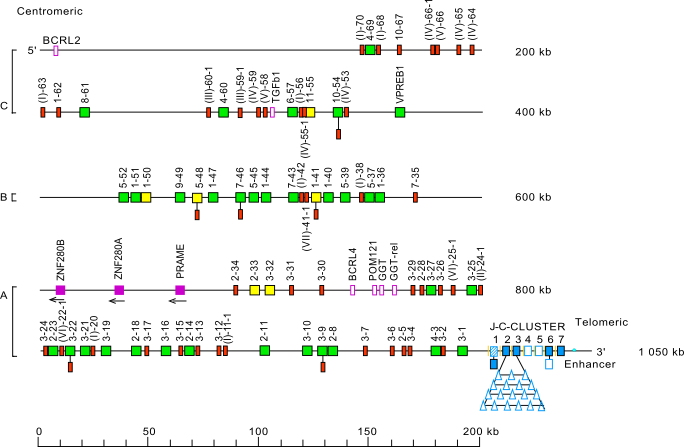
Legend:
Colors are according to IMGT color menu for genes.
The boxes representing the genes are not to scale. Exons are not shown.
A double slash // indicates a gap in genome assembly. Distances in bp (base pair) or in kb (kilobase) associated with a double slash are taken
into account in the length of the lines and included in the numbers displayed at the right end of the lines.
A, B, C refer to three distinct V-CLUSTERs based on the IGLV gene subgroup content [6].
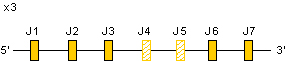
The Homo sapiens IGL J-C-CLUSTER comprises polymorphic number (from 7 to 11) of highly similar cassettes resulting from recent amplification as determined by RFLP and Southern blot. Only the J-C-CLUSTER with 7 cassettes has been sequenced so far. The numbers 1 to 7 indicate the IGLJ1-IGLC1, IGLJ2-IGLC2, IGLJ3-IGLC3, IGLJ4-IGLC4, IGLJ5-IGLC5, IGLJ6-IGLC6 and IGLJ7-IGLC7 cassettes, respectively).
Bornes of the human (Homo sapiens) IGL locus
• TOP3B (DNA topoisomerase III) (5' borne) has been identified 43 kb upstream of IGLV(I)-70 (P), the most 5' gene in the locus.
• RSPH14 (radial spoke head 14 homolog) (3' borne) has been identified 136 kb downstream of IGLC7 (F), the most 3' gene in the locus.
IGLV gene names are designated by a number for the subgroup
[4,6] followed by a dash and a number for the localization from 3' to 5' in the locus.
Pseudogenes which could not be assigned to subgroups with functional genes are designated by a roman number
between parentheses, corresponding to the clans [7],
followed by a dash and a number for the localization from 3' to 5' in the locus.
Clans (Figure IGLV clans) comprise, respectively:
- clan I: IGLV1, IGLV2, IGLV6 and IGLV10 subgroup genes, and pseudogenes IGLV(I)-20, -38, -42, -56, -63, -68 and -70
- clan II: IGLV3 subgroup genes
- clan III: IGLV7 and IGLV8 subgroup genes
- clan IV: IGLV5 and IGLV11 subgroup genes, and pseudogenes IGLV(IV)-53, -59, -64, -65 and -66-1
- clan V: IGLV4 and IGLV9 subgroup genes, and pseudogenes IGLV(V)-58 and -66
- clan VI: pseudogenes IGLV(VI)-22-1 and -25-1
- clan VII: pseudogene IGLV(VII)-41-1
IGLV(IV)-66-1 has been identified in D87004 by IMGT curators (G. Folch, V. Giudicelli, M.-P. Lefranc).
IGLV(VI)-25-1 has been identified in D86994 by IMGT curators (N. Bosc, M.-P. Lefranc).
IGLV(III)-60-1, IGLV(III)-59-1, IGLV(IV)-55-1 and IGLV(II)-24-1 were added to the Locus representation on 26/05/2020 (G. Folch and M-P. Lefranc).
Locus representation with only the functional genes: human (Homo sapiens) IGL locus on chromosome 22 (22q11.2)
Gene localization is according to data from IMGT/LocusView. This locus representation with only the functional genes is used with IMGT/GeneFrequency.

* When needed, indicate the presence of allele(s) with another functionality: see above human (Homo sapiens) IGL locus on chromosome 22 (22q11.2)
Zoom for IGLJ genes
- [1] Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G., The immunoglobulin FactsBook, Academic Press, London, 458 pages (2001). 012441351X
- [2] Lefranc, M.-P., Nomenclature of the human immunoglobulin genes, Current Protocols in Immunology, A.1P.1-A.1P.37 (2000).
- [3] Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G., Immunoglobulin lambda (IGL) genes of human and mouse, In: Molecular Biology of B cells (Honjo, T., Alt, F.W. and Neuberger, M.S. eds), Academic Press, Elsevier Science, pp. 37-59 (2004). 0120536412
- [4] Frippiat, J.-P. et al., Hum. Mol. Genet., 4, 983-991 (1995).
- [5] Kawasaki, K. et al., Genome Res., 5, 125-135 (1995).
- [6] Williams, S.C., Frippiat, J.-P. et al., J. Mol. Biol., 264, 220-232 (1996).
- [7] Kawasaki, K. et al., Genome Res., 7, 250-261 (1997).
- [8] Hieter, P.A. et al., Nature, 294, 536-540 (1981).
- [9] Taub, R.A. et al., Nature, 304, 172-174 (1983).
- [10] Dariavach, P. et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 84, 9074-9078 (1987).
- [11] Vasicek, T.J. and Leder, P., J. Exp. Med., 1990, 609-620 (1990).
- [12] Taub, R.A. et al., Nature, 304, 172-174 (1983).
- [13] Ghanem, N. et al., Exp. Clin. Immunogenet., 5, 186-195 (1988).
- [14] Kay, P.H. et al., Immunogenetics, 35, 341-343 (1992).
- [15] Lefranc, M.-P. et al., Hum. Genet., 104, 361-369 (1999).
- [16] Lefranc, M.-P. et al., Hum. Genet., 104, 361-369 (1999).
- [17] Blomberg, B.B. et al., J. Immunol., 147, 2354-2358 (1991).
- [18] Asenbauer, H. et al., Eur. J. Immunol., 29, 713-724 (1999).
- [19] Combriato, G. and Klobeck, H.G., J. Immunol., 168, 1259-1266 (2002).
Links to IMGT/LocusView, IMGT/GENE-DB and genome browsers
- Genome browsers:
- Created:
- 04/07/2003
- Last updated:
- 22/09/2023
- Authors:
- Nathalie Pallarès, Nathalie Bosc and Marie-Paule Lefranc
