
| Disulfide bridges | Chain | Classes and subclasses | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgD | IgG | IgA | IgE | |||||||
| IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 | IgG4 | IgA1 | IgA2 | ||||||
| Inter H-L | H (1) | Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1? |
| Positions | CH1: 10 | CH1: 11 | h 5 | CH1: 10 | CH1: 10 | CH1: 10 | CH1: 10 | CH1: 123 | CH1: 10, 11 | ||
| L (2) | C-KAPPA | 126 (last residue) | |||||||||
| C-LAMBDA | 126 (last-but-one residue) | ||||||||||
| Inter H-H | H (1) | Number | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 11 | 2 | 2? | 2? | 1? |
| Positions | CH2: 125 | CH2: 1.6 | h 11, h 14 | h 4, h 5, h 8, h 11 | H1: h 13, h 16 H2: h 5, h 11, h 14 H3: h 5, h 11, h 14 H4: h 5, h 11, h 14 |
h 8, h 11 | CH2: 1.1, 1.2 | CH2: 1.1, 1.2 | CH2: 1.6, 11, 124 | ||
In INN, cysteines of the hinge involved in inter-chain bridges are indicated with a small letter 'h', for example, for an Homo sapiens IgG1 - kappa: Inter-H-L (h 5-CL 126), Inter-H-H (h 11, h 14).
| Disulfide bridges | Chain | Classes and subclasses | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM | IgD | IgG | IgA | IgE | |||||||
| IgG1 | IgG2A | IgG2B | IgG2C | IgG3 | |||||||
| Inter H-L | H (1) | Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1? | 1 |
| Positions | CH1: 10 | CH1: 10 | h 5 | CH1: 11 | CH1: 11 | CH1: 11 | CH1: 11 | CH1: 123 CH2: 1.1 |
CH1: 10 | ||
| L (2) | C-KAPPA | 126 (last residue) | |||||||||
| C-LAMBDA | 126 (last-but-one residue) | ||||||||||
| Putative inter H-H | H (1) | Number | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | ? | 2 |
| Positions | CH2: 125 | no H-H bridge | h 7, h 10, h 12 | h 10, h 13, h 15 | h 12, h 15, h 18, h 21 | h 11, h 17, h 20 | h 15 | ? | CH2: 11, 124 | ||
In INN, cysteines of the hinge involved in inter-chain bridges are indicated with a small letter 'h', for example, for a Mus musculus IgG2B - kappa: Inter-H-L (CH1 11-CL 126), Inter-H-H (h 12, h 15, h 18, h 21).
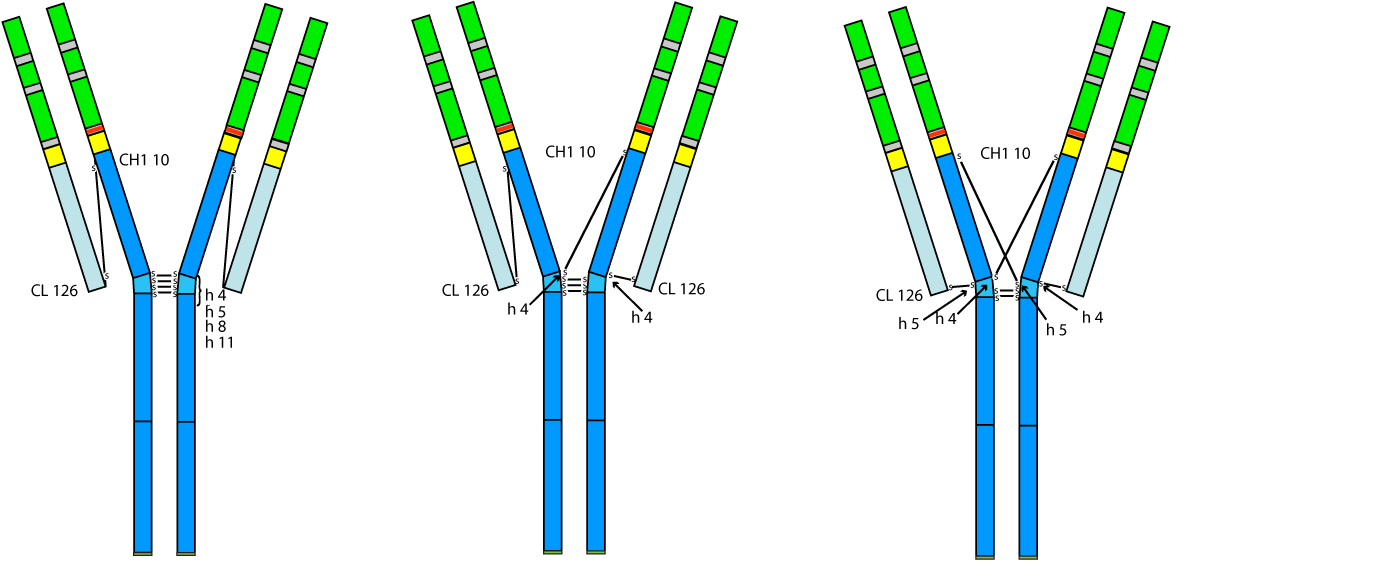
Three isoforms of the Homo sapiens IgG2 have been identified which differ by their inter-chain disulfide bridges [1, 2, 3].
The isoform A is classically characterized by:
- two inter H-L (CH1 10-CL126) (one for each Fab arm)
- four inter-H (h 4, h 5, h 8, h 11) disulfide bridges
In the isoform A/B, one of the two inter-H-L (CH1 10-CL 126) on one Fab arm and the inter-H-H (h 4 - h 4) are replaced by an inter-H-H (h 4 - CH1 10) and an inter-H-L (h 4 - CL 126).
The isoform B is characterized by an additional change, the inter-H-L (CH1 10 - CL 126) on the second Fab arm and the inter-H-H (h 5 - h 5) being replaced by an an inter-H-H (h 5 - CH1 10) and an inter-H-L (h 5 - CL 126).
The isoform A is predominant for IgG2-lambda, the isoform A/B is equally represented for both IgG2-kappa and IgG2-lambda, whereas in contrast the isoform B is only found for IgG2-kappa, not for IgG2-lambda [1, 2]. As CL 126 is terminal for C-KAPPA and subterminal for C-LAMBDA, it has been proposed that the presence of the serine in 127 of the lambda chain may sterically interferes with the formation of the disulfide bridge [2].
Disulfide bridges of the Homo sapiens IgG2 disulfide isoforms
| Isoform A | Isoform A/B | Isoform B |
|---|---|---|
| Inter-H-L (CH1 10 - CL' 126) | Inter-H-L (CH1 10 - CL' 126) | Inter-H-L (h 5'' - CL' 126) |
| Inter-H-L (CH1'' 10 - CL''' 126) | Inter-H-L (h 4'' - CL''' 126) | Inter-H-L (h 4'' - CL''' 126) |
| Inter-H-H (h 4 - h'' 4) | Inter-H-H (h 4 - CH1'' 10) | Inter-H-H (h 4 - CH1'' 10) |
| Inter-H-H (h 5 - h'' 5) | Inter-H-H (h 5 - h'' 5) | Inter-H-H (h 5 - CH1 10) |
| Inter-H-H (h 8 - h'' 8) | Inter-H-H (h 8 - h'' 8) | Inter-H-H (h 8 - h'' 8) |
| Inter-H-H (h 11 - h'' 11) | Inter-H-H (h 11 - h'' 11) | Inter-H-H (h 11 - h'' 11) |
It is not excluded that other disulfide bridges may occur between the same cysteines.
Schematic representation of the IgG2 disulfide isoforms
| Isoform A | Isoform A/B | Isoform B |
| (1) | H: heavy chain |
| (2) | L: light chain (kappa or lambda) |
See also: