
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB and IMGT/2Dstructure-DB Documentation
IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®

IMGT/3Dstructure-DB and IMGT/2Dstructure-DB Documentation
IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®

IMGT/3Dstructure-DB [1] is part of IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®, the high-quality integrated information system specialized in immunoglobulins (IG), T cell receptors (TR), major histocompatibility complex (MHC) of human and other vertebrates species, immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), MHC superfamily (MhcSF) and related proteins of the immune system (RPI), created in 1989 by Marie-Paule Lefranc (Laboratoire d'ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire, LIGM, Université Montpellier II and CNRS) and on the Web since July 1995. IMGT/3Dstructure-DB is the IMGT three-dimensional (3D) structure database.
In 2008, amino acid sequences from INN/WHO were entered in IMGT/2Dstructure-DB, a section of IMGT/3Dstructure-DB. They comprise those of monoclonal antibodies (IG, mAb) and fusion proteins for immune applications (FPIA).
In 2010, amino acid sequences from Kabat were entered in IMGT/2Dstructure-DB. They comprise those of immunoglobulin superfamily sequences collected and manually culled from the scientific literature, especially the book "Sequences of proteins of immunological interest, Vol.I and II", U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institute of Health.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB provides a unique expertised resource on IG, TR, MH and RPI with known
3D structures. Structural data are extracted from the Protein
Data Bank PDB. The IMGT/3Dstructure-DB standardized information includes IMGT annotation
on the sequences, 2D structures (IMGT Colliers de Perles) and 3D structures of IG, TR, MH,
and RPI with known 3D structures which are available in IMGT/3Dstructure-DB cards [2-7].
Annotations are according to the IMGT Scientific chart
rules based on the IMGT-ONTOLOGY concepts [8-10].
Three-dimensional structure analysis includes chain details and contact analysis at different
levels (domain internal stability, domain/chain interface, residue) that are particularly
relevant for immunological proteins like IG, TR and MH, as they interact specifically with
a great number of molecules.
Domain sequences are renumbered according to the IMGT unique numbering for V-DOMAIN and V-LIKE-DOMAIN [11], to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN and C-LIKE-DOMAIN [12], and/or to the IMGT unique numbering for G-DOMAIN and G-LIKE-DOMAIN [13]. Each IMGT/3Dstructure-DB card is associated to a coordinate flat file with IMGT renumbered residues.
Screenshots are in blue rectangles and data processing details are in green rectangles.
The screen captures have been updated, please note the text has not yet been updated.
The IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Query page shows, at the top of the page, the status of the database (Current date, the total number of entries and its decomposition (PDB, INN) and the date of the last update) and at the bottom of the page, the last entries and the access to the IMGT tools (IMGT/DomainDisplay, IMGT/Collier-de-Perles, IMGT/DomainGapAlign, IMGT/DomainSuperimpose and IMGT/mAb-DB).

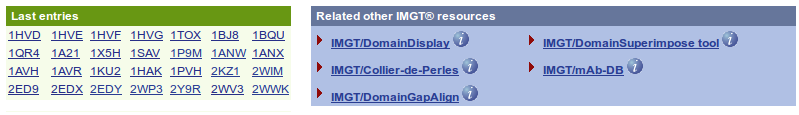
The IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Query page allows six types of search, the possibility to align user's sequences against whole IMGT/3Dstructure-DB entries using FASTA and offers visualization choice for the results.
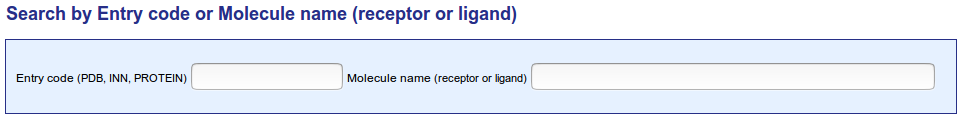
The IMGT/3Dstructure-DB entry code (ID) is identical to the PDB code, INN code or PROTEIN code. PDB code is an alphanumeric code (Ex : 1ao7), INN code is a numeric code (Ex: 7637) while PROTEIN code is an alphanumeric code which lenght is equals to 6 (Ex : p00054).
An AutoComplete behavior is available for this field. AutoComplete works in the following manner: as you type in the beginning of a PDB code previous entries are pulled from a storage area and you may elect to simply select one of these entries. By selecting an entry, you no longer have to input the string because AutoComplete finishes entering the string for you.
IG, TR, MH or RPI protein name and, if present, ligand. An IMGT molecule name is either a name retrieved from the literature or a name modified by IMGT® or a name added by IMGT®. The search by IMGT molecule name is case insensitive.
The query "%>%" will retrieve all protein mutants for which the amino acid change(s) are indicated with the signe '>' in the IMGT molecule name.
IMGT molecule naming rules
IG and TR: When the molecule name is undefined in the PDB file, an IMGT standardized name is created which comprises letter(s) and number(s) for the fragment type and the chain type, and if necessary, a hyphen followed by a number (ex: CH2E-1, FcE-1, FcE-2, FcG1-1, FcG1-2, FcG1-3, Fv-1, FabM).w
Mutants: IMGT standardized names for the protein mutants (ex: mutants of Len and Rei) comprise amino acids changes described according to the IMGT description of mutations (IMGT Scientific chart).
Particularities in protein designations: The designation 'Newm' is used, in IMGT/3Dstructure-DB (ID: 7fab) for the human IgG1 myeloma protein Fab (designated as 'New' in PDB). This IMGT® designation Newm avoids confusion with the human 'New' Bence Jones Protein, that has been sequenced before 'Newm' (Particularities in protein designations: Human immunoglobulins: New and Newm).
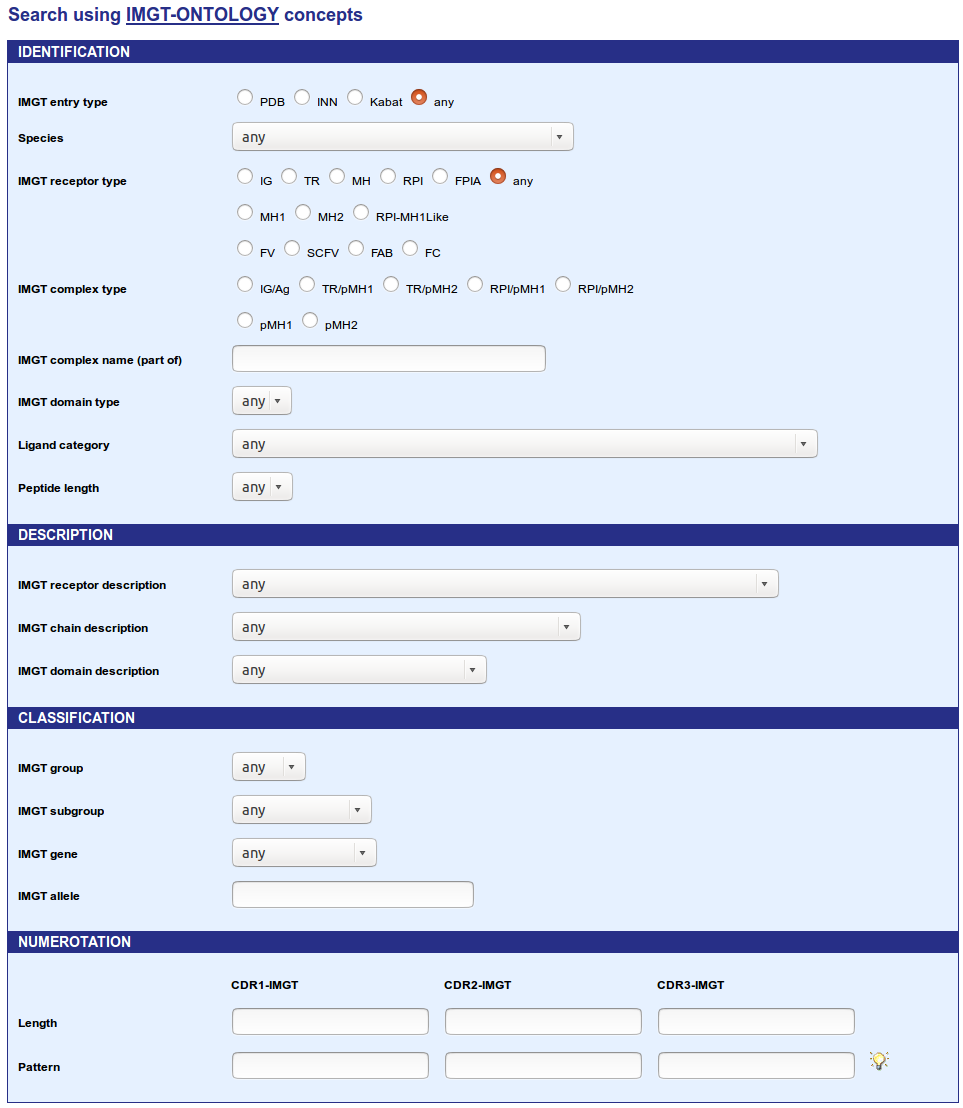
This section allows users to search entries using the IMGT-ONTOLOGY concepts (IDENTIFICATION, DESCRIPTION, CLASSIFICATION and NUMEROTATION) for each type of IMGT entry. This kind of search uses linked select elements. Linked select elements are two or more selects, where choosing a value in one changes the available values in some of the rest. For example, selecting an IMGT receptor type will updates the 'IMGT receptor description' select to only contain receptor description from the IMGT receptor type selected. In the same way, selecting an IMGT group will updates the 'IMGT subgroup' select to only contain subgroup(s) from the IMGT group selected.
Choose an IMGT entry type and then a: Species (also includes Camelized, Chimeric, Humanized, Caninized and Synthetic), IMGT receptor type (IG, TR, MH, RPI, FPIA or Any), IMGT receptor description, IMGT chain description, IMGT group, IMGT subgroup, IMGT gene or IMGT allele.
Definitions
A Chimeric receptor is one of which all chains are chimeric as a result of protein engineering. A chimeric chain is a chain that contains a foreign region (originating from one species other than human, or synthetic) linked to another region of different species. Note that the definition of a chimeric antibody is more precise.
A Humanized receptor is one of which all chains are humanized as a result of protein engineering. A humanized chain is a chain in which a region is foreign (originating from one species other than human, or synthetic) whereas the remaining chain is of human origin. Note that the definition of a humanized antibody is more precise. 'Camelized', 'Chimeric', 'Humanized' and 'Synthetic' refer to both the receptor and to its chain(s).
Options menus allows you to refine your research (MH1 and MH2 for IMGT receptor type; FV, SCFV, FAB, FC and RPI-MH1Like for IMGT receptor description).
IMGT Complex type
Search by Complex type can retrieve entries similar to the following complexes:
Ligand category
Search by Ligand category can retrieve structures which are in contacts with: Carbohydrate, Chemical compound, DNA, peptide, Protein or RNA.
Peptide length
Search by Peptide length can retrieve structures which are in contacts with peptide(s) whose length is chosen in the drop-down list.
IMGT description rules
IMGT receptor and chain description is based on the IMGT-ONTOLOGY DESCRIPTION concept.
IG, TR, MH or RPI receptors and chains are described with standardized labels (listed in IMGT/PROTEIN-DB and IMGT/3Dstructure-DB: standardized keywords and labels for IG, TR and MH), and defined in the IMGT Scientific chart (IMGT/PROTEIN-DB and IMGT/3Dstructure-DB: Label definitions for IG, TR and MH).
If the receptor is incomplete, the receptor label is replaced by domain or chain labels shown between parentheses.
IMGT classification rules:
Group, subgroup, gene and allele names are based on the IMGT-ONTOLOGY CLASSIFICATION concept.
IG and TR: V-GENE, D-GENE, J-GENE and C-GENE names are according to the IMGT gene nomenclature. Human and mouse IG and TR genes are from IMGT/GENE-DB. The D-GENE identification is not shown when it is too uncertain owing to the shortness of the D sequences in the V-D-J rearrangement, to N-region diversity and/or, for the IG, to somatic hypermutations.
MH: The closest gene(s) is (are) provided for the rodent MH.
Allele:
IG and TR: The closest allele(s) is (are) provided for each gene. Human and mouse alleles are from IMGT/GENE-DB. Alleles are displayed in IMGT Alignments of alleles and IMGT/DomainDisplay.
MH: The closest allele(s) is (are) provided for the human MH (HLA).
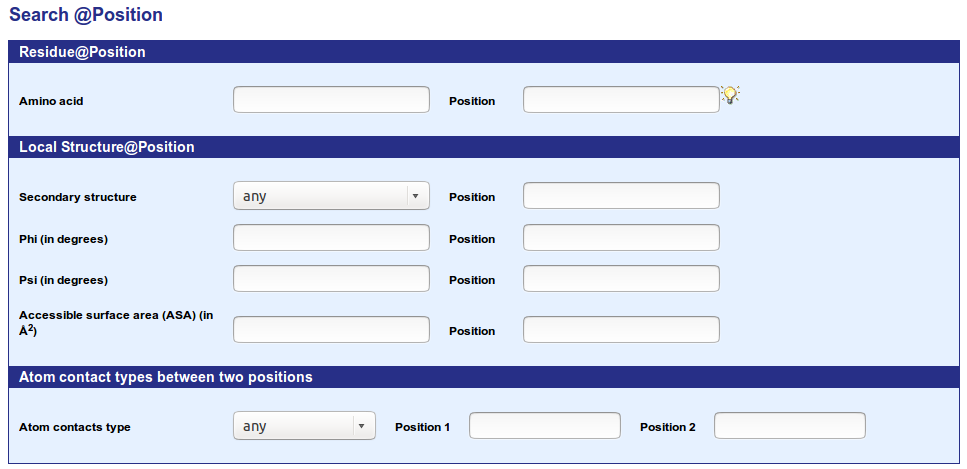
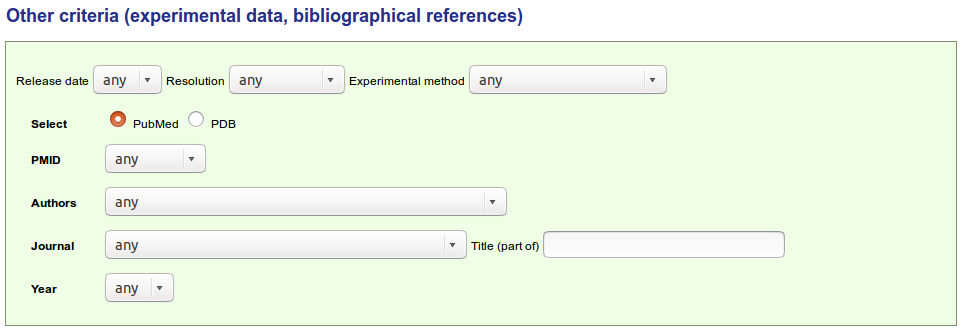
The form allows an easy search by the following criteria:

A complex query can be performed. It is made up of a list of structural criteria
coordinated by parentheses and boolean operator (AND and OR).
The query can be entered in the text area, either manually, or with the Javascript
helper tool (available below the text area). The selection of a structural criteria
in the scrolling list of the helper tool will show the corresponding fields to be filled in.
A 'Quick Help' is available for each criterion.
The different criteria currently implemented are:
At the top of the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Query page, the user can choose to view the results as "Overview" or "Domain and sequence alignment". These two choices will display a list of IMGT/3Dstructure-DB entries or a list of chains respectively. .
The Overview offers many choices:
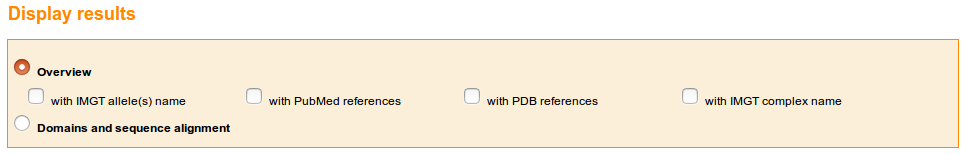
An additional choice, "Reference view" is available at the bottom of the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Reference query page.
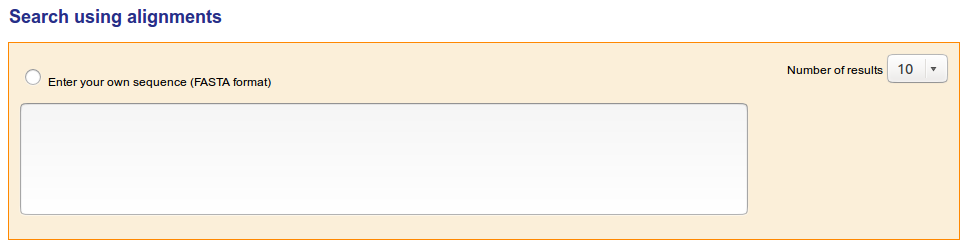
Users can FASTA their own sequences against the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB sequences using the 'Search using alignments' tool. Users can choose the numbers of results to display
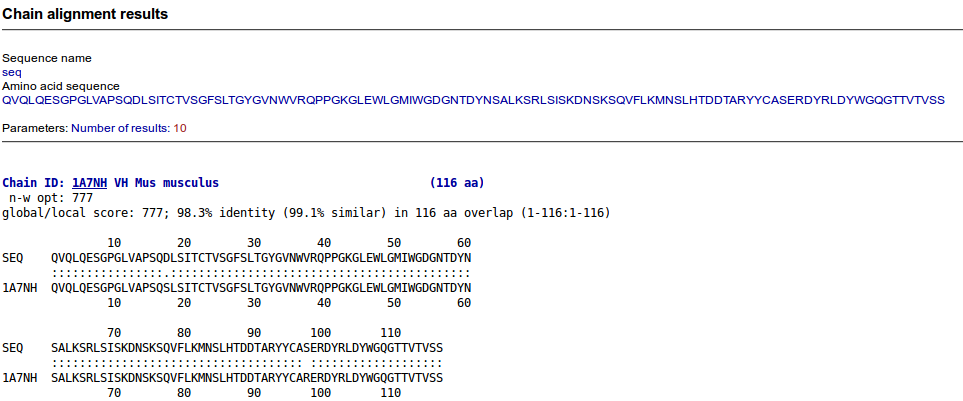
The result presentation depends on the visualization choice made at the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Query page. On top of each result page, the visualization choice and the query are recalled, and the number of results is shown. For results which correspond to a list of chains (and not to a list of entries) it is recalled, between parentheses, that the number of results correspond to the 'number of chains containing the selected domain or region'. An additional result presentation corresponds to 'References'. The list of results is sorted by ID (entry or chain).
The 'Overview' results provide a list of Entries.
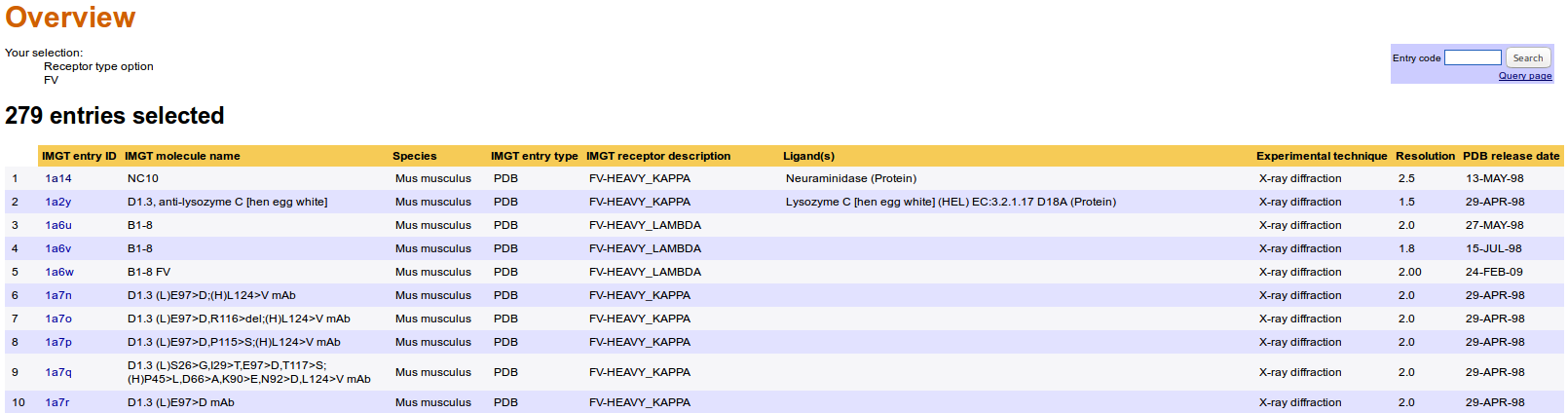
The Overview results page displays IMGT/3Dstructure-DB entries that satisfy the query, with for each entry the following information:
The 'Domain type sequences' results provide a list of chains containing the selected domain type.
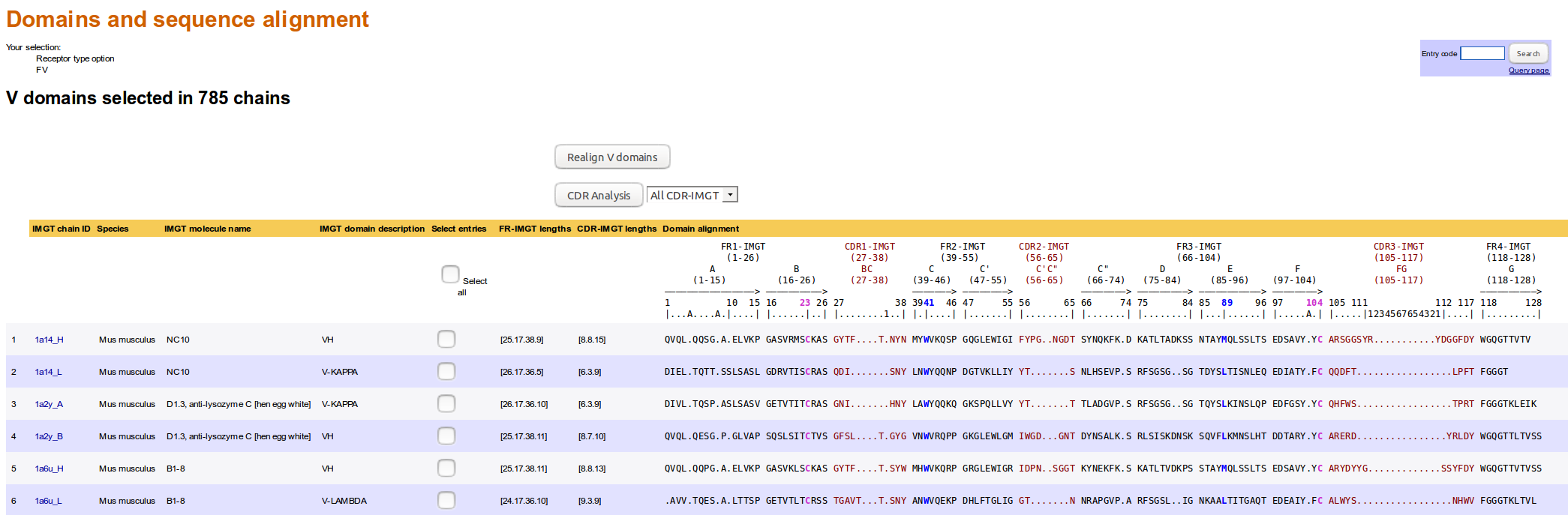
The 'Domain and sequence alignment' result page displays a list of IMGT/3Dstructure-DB chains with, for each chain:
'Reference view' is only available from the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Reference query page.
It displays the following fields for bibliographical references extracted from the coordinate file:
IMGT entry ID, Authors (PDB), Title (PDB), Year (PDB), Authors (PubMed), Title (PubMed) and Year (PubMed).
Clicking on the IMGT entry ID gives access to the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB card.
The 'IMGT/3Dstructure-DB card' is the core unit of IMGT/3Dstructure-DB. Indeed, there is one card per IMGT/3Dstructure-DB entry and this card provides access to all data related to that entry.
The IMGT/3Dstructure-DB card header contains:
For PDB entries, a summary table with:
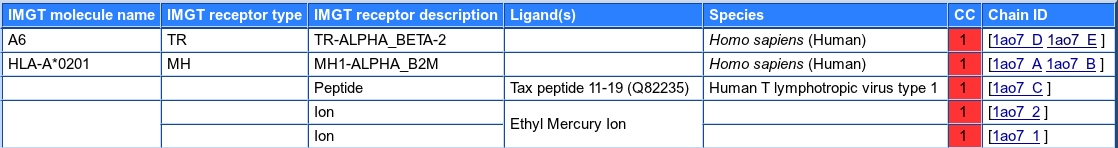
For INN entries, a summary table with:

Below the summary table are added:
Identification of the chains belonging to the same protein quaternary structure
Chains belong to the same protein quaternary structure when they are of the same type (IG, TR, MH or else), their amino acid sequence length is of the same order (no peptide with huge protein) and have at least 60 amino acids contacts and eventually a covalent link (as identified by the coordinate file). A manual expertise is sometimes required to correct errors created by these very simple rules and in some intricate cases.
Seven or eight (if Paratope and epitope are present) tabs give access to:


The Results from 'Paratope and epitope', 'Chain details' and 'Contact analysis' are detailed in the next sections.
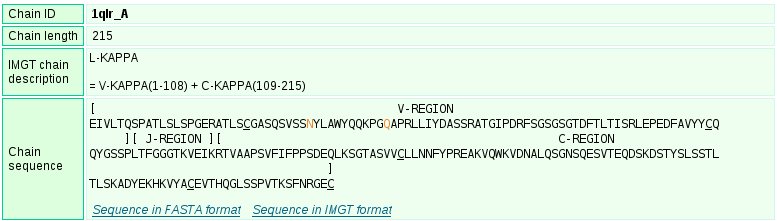
The 'Chain details' comprise information first on the chain itself, then per domain. The 'Chain details' section also gives information on associated ions and/or molecules that include ions, water and chemical molecules other than proteins or nucleic acids.
Identification of the '(N-D)-REGION' region
The '(N-D)-REGION' is arbitraly delimited by the lengths of the untrimmed germline V-REGION and J-REGION. If nucleotide sequences are available, it is recommended to use IMGT/V-QUEST for an accurate delimitation and analysis of the junction.
If javascript is enabled on your browser, every residue (except those in italic) is clickable and gives access to its IMGT Residue@Position card.
The links Sequence in FASTA format and Sequence in IMGT format are for
The different domains which are parts of a chain, are described in details in a similar format. They include:

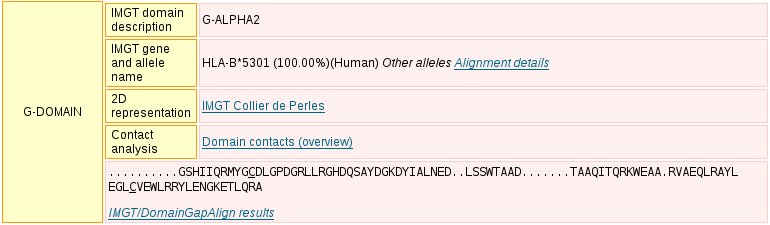
The display includes, for each domain:
Notion of consensus between alleles
Consistency between alleles regions of the same chain is taken into account through the field consensus. Indeed several alleles may correspond to the same region but some of these alleles may not be consistent with the alleles in other regions. For example, alleles identified for different DOMAINs of a REGION must be identical.
IMGT Colliers de Perles are 2D graphical representation of the domains based on the IMGT unique numbering.
IMGT Colliers de Perles are provided for V, C and G type domains. For the V and C type domains, they represent the immunoglobulin fold topology. Loops anchors are shown in square, highly conserved amino acids at a position are in red and hydrophobic positions found as hydrophobic in more than 80% such domain sequences are in blue. For the V type domains the CDR-IMGT lengths are written at the top of the page between brackets and they are colored according to the IMGT Scientific chart. In IMGT Colliers de Perles on 2 layers, hydrogen bonds are shown on the front layer, back layer and between the 2 layers.
Clicking on the residue in the IMGT Colliers de Perles gives access to The "IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Residue@Position" card.
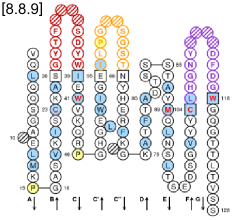
IMGT Collier de Perles on one layer (chain 1bql_H V-DOMAIN)
|
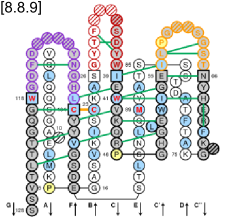
IMGT Collier de Perles on two layers (chain 1bql_H V-DOMAIN)
|
|
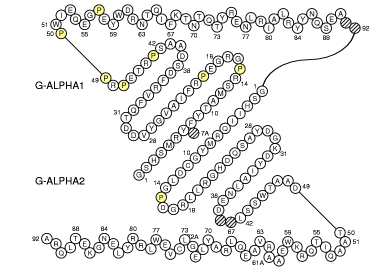
IMGT Collier de Perles of MH class I (chain 1a1m_A)
|
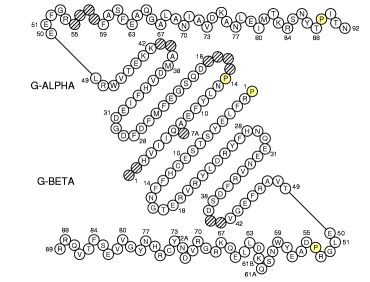
IMGT Collier de Perles of MH class II (chain 1a6a_A II-ALPHA and 1a6a_B II-BETA)
|
Note that ions and/or molecules are individualized in IMGT when they are included by error in the PDB chain definition.
Carbohydrate chains and molecules of particular interest
Although carbohydrates are usually linked covalently to the amino acid chains, they are considered separately as a carbohydrate chain from the amino acid chain in the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB card.
IMGT chain ID is assigned to molecules of particular interest (for example inorganic antigene, heme molecule, etc.). This allows to distinguish these molecules from solvant and ions and to view them in the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB card summary table and in the IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contact analysis cards.
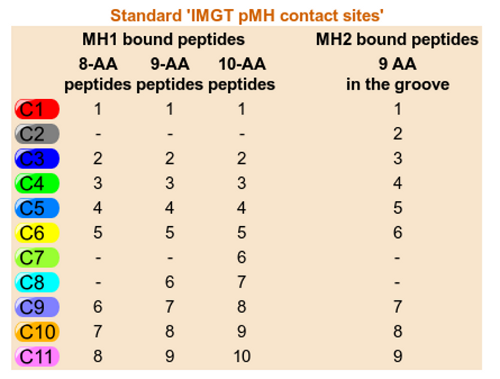
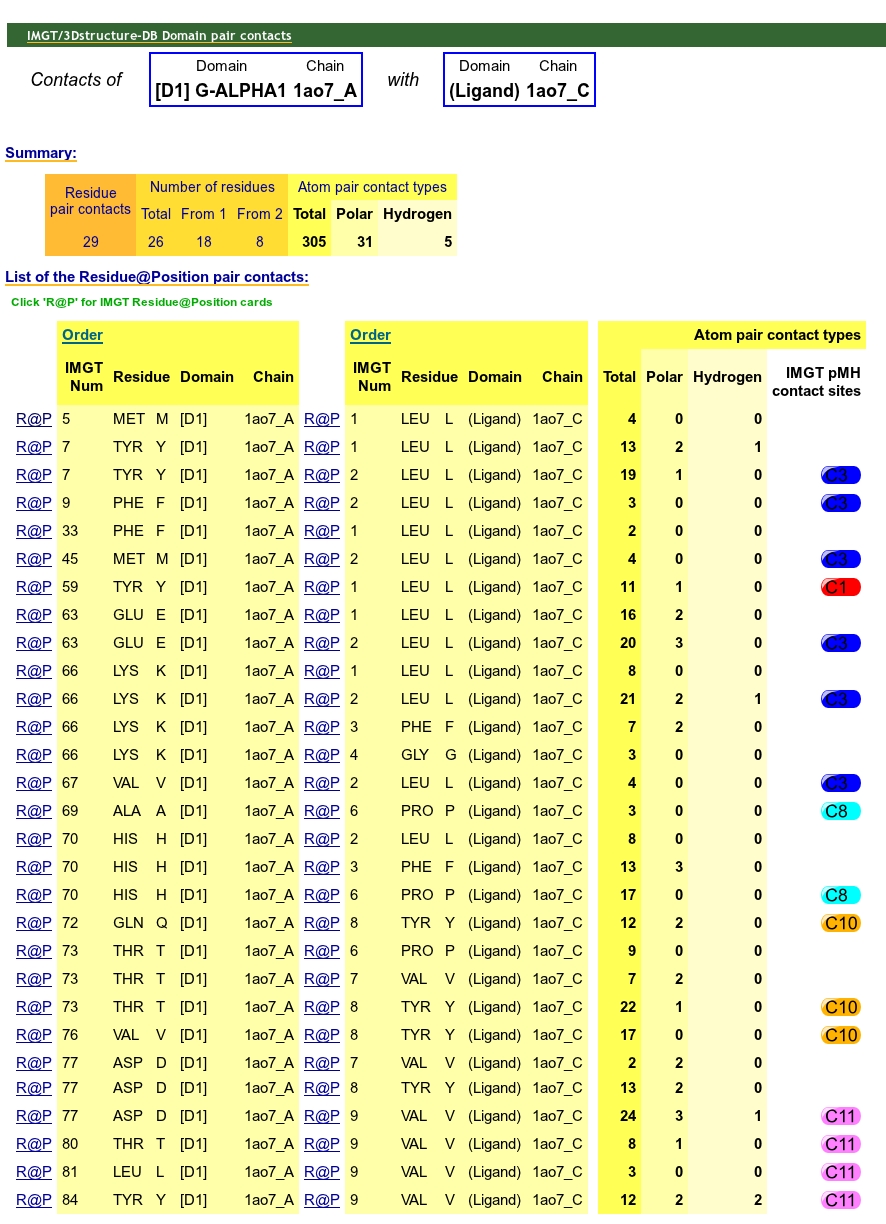
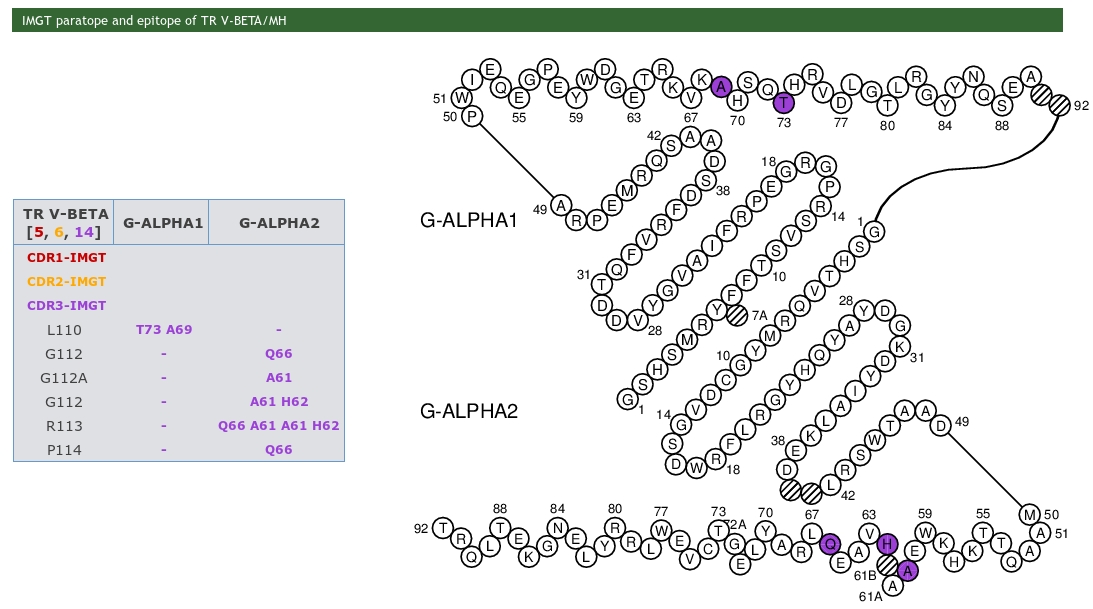
IMGT pMH contact sites provide IMGT Collier de Perles for G-DOMAIN with identification
of the eleven IMGT contact sites for the standardized analysis of
the peptide/MH contacts 7.
The user can also download the table. The download contains two files. The first one provided chains details on a text file and the second one is the contact table on csv format.
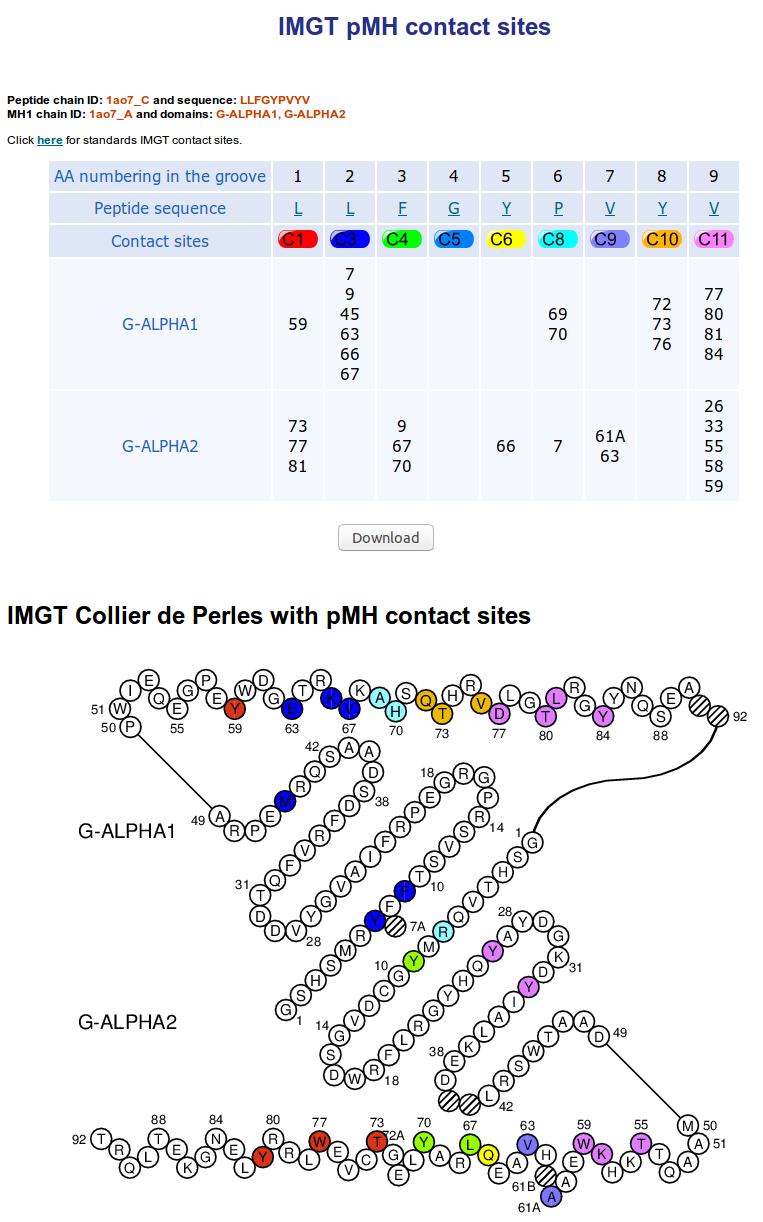
The IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Domain contacts (overview) analysis provides information on the contacts between domain and/or chain and on the internal contacts in an IMGT/3Dstructure-DB entry.
The domain/chain partners considered are designated as 'Set 1' and 'Set 2'. The number of residue contacts, the number of residues involved (total and per partner 1 and 2) and the number of atom contact types are provided.
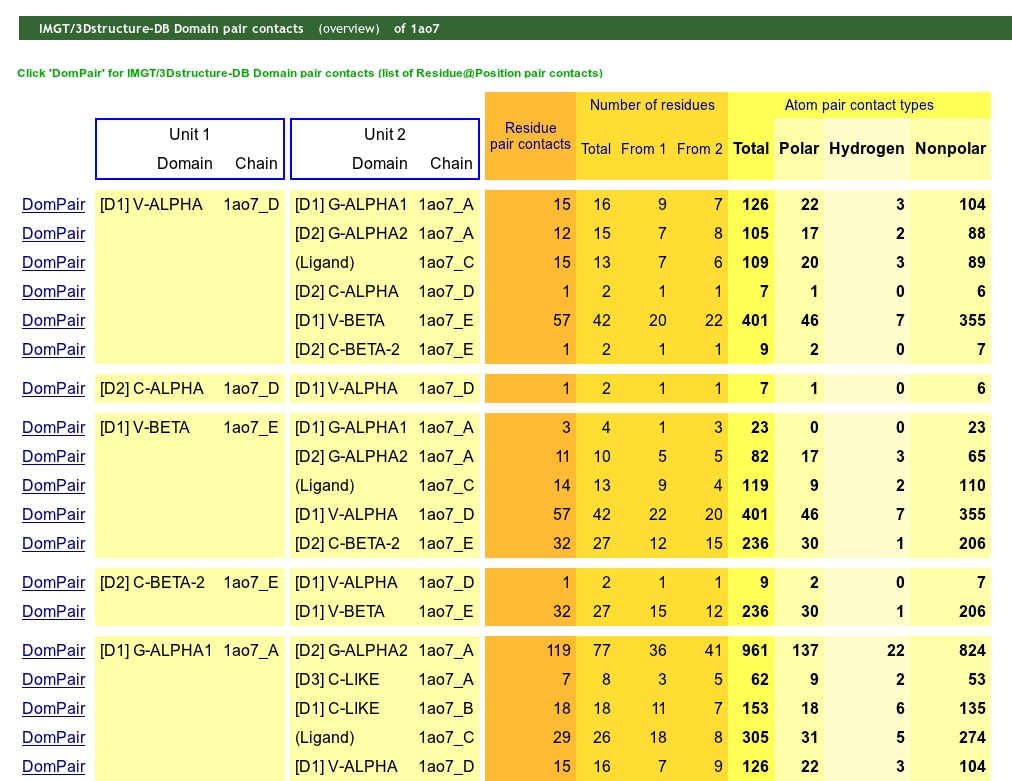
Clicking on "DomPair" gives access to the 'IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Domain pair contacts of the selected pair of partners.
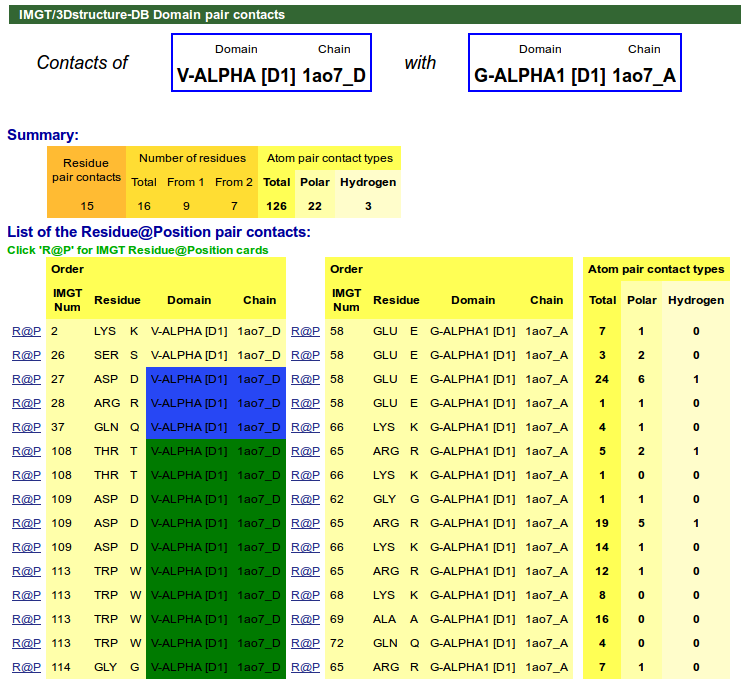
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Domain pair contacts provides information on the contacts between a pair of partners (indicated at the top of the page). Clicking on R@P gives access to the IMGT Residue@Position card (4.2.1 section).
For TR/pMH complexes, IMGT pMH contact sites are available in IMGT/3Dstructure-DB Domain pair contacts.

If Javascript is enabled on your browser the IMGT Residue@Position card is accessible by clicking on a residue either in the amino acid sequence or in the IMGT Collier de Perles.
A Residue@Position is a residue at an IMGT position, according to the IMGT unique numbering.
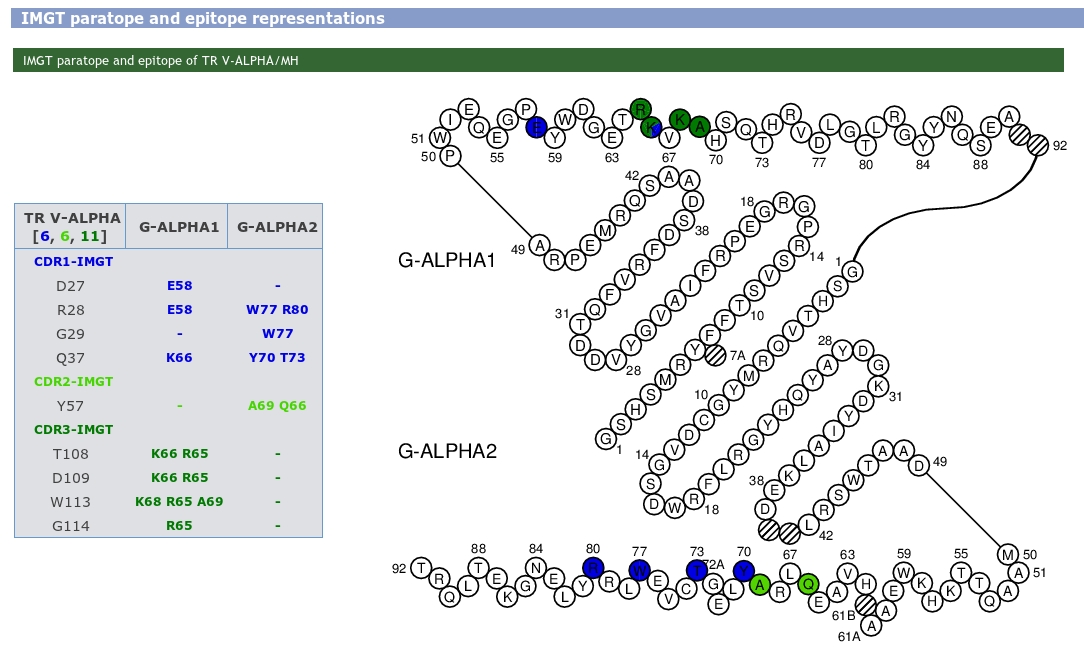
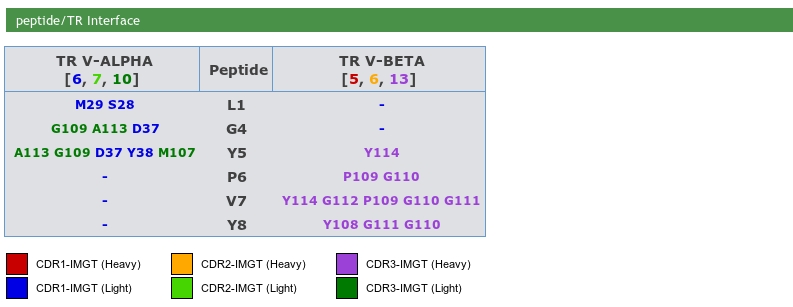
A Residue@Position is defined by:Epitope description of IG/antigene, TR/peptide and TR/MH are provided. The MH/peptide interface is also provided in this section.

IMGT paratope and epitope representations are also provided and display the amino acids implicated in pMH and TR/pMH complexes. The amino acids are shown as tables and in IMGT Colliers de Perles.

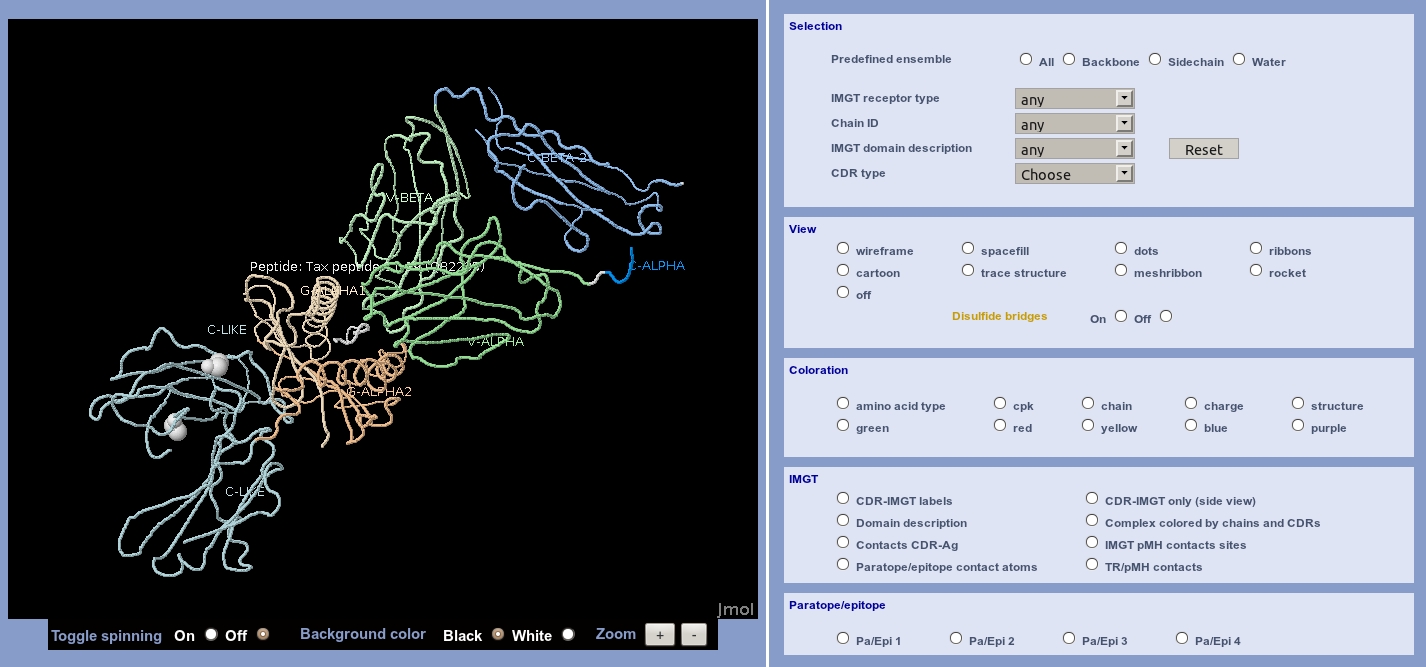
The whole chain sequences are displayed in a box, indicating the chain ID, the IMGT Receptor description and the length of the chain. Users just have to click on a residue in sequences to visualize it in the JSmol (wireframe by default).

Users can view structures/molecules using a JSmol. The interface is composed of 5 sub-menus: Selection, View, coloration, IMGT and Paratope/epitope.
The Selection menu offers a selection by:
Receptor type, Chain ID, Domain description and CDR type are linked select elements.
Linked select elements are two or more selects, where choosing a value in one changes the available values
in some of the rest.
For example, selecting an IMGT receptor type will updates the 'Chain ID' select
to only contain Chain ID from the IMGT receptor type selected.
In the same way, selecting a Chain ID will
updates the 'IMGT domain description' select to only contain domain descriptions from the Chain ID selected.
The View menu offers a display in the:
The Coloration menu offers a display:
The IMGT menu offers different displays, depending on the type and the receptor description of the structure, and using IMGT concepts:
The Paratope/epitope menu offers visualization of the different amino acids implicated in the choosen complex.
Allows to view (or download) an IMGT coordinate file renumbered according to the IMGT
unique numbering.
In the IMGT coordinate file the 'REMARK 410' lines which have been added provide
IMGT specific information (IMGT molecule name, IMGT receptor description and chain codes),
domain positions (with CDR-IMGT length for V type domains) and regions position and allele
identification.
For Windows users, the gziped renumbered coordinate file is automatically unziped by the system. You just have to remove the .gz extension.

Since version 4.3.0, the upgrade and new versions of IMGT/3Dstructure-DB and tools are indicated in the two files:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 2246 entries (1820 PDB, 81 INN and 345 Kabat).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1881 entries (1800 PDB and 81 INN).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1855 entries (1775 PDB and 80 INN).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1835 entries (1765 PDB and 70 INN).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1753 entries (1698 PDB and 65 INN).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1655 entries (1616 PDB and 39 INN).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1609 entries (1570 PDB and 39 INN).
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1487 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1441 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1403 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1303 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1275 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1269 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1265 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB has been upgraded for multiple structures and with new functionalities:
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1221 entries.
IMGT/3Dstructure-DB contains 1209 entries.
The first gene identification of the human IG proteins were carried out during a stay in the Laboratoire d'ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire, IGH, CNRS, Montpellier, France, by Dr. Gunilla Norhagen and Dr. Per-Erik Engstrom (May 1998) from the Huddinge University Hospital, Karolinska Institute, Huddinge, Sweden, Dr. Oksana Kravchuk (April-May 1999) from the Research Centre for Medical Genetics, Russian Academy of Medical Science, Moscow, Russia, and Dr. Olga Posukh (April-July 1999, July-October 2000) from the Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Science, Novosibirsk, Russia.
| [1] | Kaas, Q., Lefranc, M.-P., IMGT/3Dstructure-DB and IMGT/StructuralQuery: a database and a tool for immunoglobulin, T cell receptor and MHC structural data, Nucleic Acid Res., 32:D208-D210 (2004). PMID:14681396. |
| [2] | Ehrenmann F., Kaas Q. and Lefranc M.-P., IMGT/3Dstructure-DB and IMGT/DomainGapAlign: a database and a tool for immunoglobulins or antibodies, T cell receptors, MHC, IgSF and MhcSF, Nucleic Acid Res., 38:D301-D307 (2010). PMID:19900967. |
| [3] | Kaas, Q. and Lefranc, M.-P., IMGT/StructuralQuery: a tool for structural data analysis of immunoglobulin and T cell receptor variable domains, ECCB 2003 |
| [4] | Kaas, Q. and Lefranc, M.-P., IMGT/3Dstructure-DB for immunoglobulin, T cell receptor and MHC structural data, ECCB 2002 |
| [5] | Ruiz, M., Analyse bioinformatique standardisée IMGT des relations séquence-structure des immunoglobulines et des récepteurs T, Thèse de doctorat, Université Montpellier II, 2001 |
| [6] | Kaas, Q., Analyse structurale des recepteurs d'antigenes dans IMGT et modelisation moleculaire, Thèse de doctorat, Université Montpellier II, 2005 |
| [7] | Ruiz, M. and Lefranc, M.-P., IMGT gene identification and Colliers de Perles of human immunoglobulins with known 3D structures, Immunogenetics, 53:857-883 (2002). PMID:11862387. |
| [8] | Kaas, Q. and Lefranc M.-P., T cell receptor/peptide/MHC molecular characterization and standardized pMHC contact sites in IMGT/3Dstructure-DB, In Silico Biology, 5:0046 (2005). |
| [9] | Giudicelli, V. and Lefranc M.-P., Ontology for immunogenetics: the IMGT-ONTOLOGY, Bioinformatics, 15:1047-1054 (1999). |
| [10] | Lefranc, M.-P. , Giudicelli, V., Ginestoux, C., Bosc, N., Folch, G., Guiraudou, D., Jabado-Michaloud, J., Magris, S., Scaviner, D., Thouvenin, V., Combres, K., Girod, D., Jeanjean, S., Protat, C., Yousfi-Monod, M., Duprat, E., Kaas, Q., Pommie, C., Chaume, D. and Lefranc G., IMGT-ONTOLOGY for immunogenetics and immunoinformatics. In Silico Biology, 4:17-29 (2004). |
| [11] | Lefranc, M.-P., Clement, O., Kaas, Q., Duprat, E., Chastellan, P., Coelho, I., Combres, K., Ginestoux, C., Giudicelli, V., Chaume, D. and Lefranc G., IMGT-Choreography for Immunogenetics and Immunoinformatics, In Silico Biology, 5:45-60 (2005). |
| [12] | Lefranc, M.-P., Pommié, C., Ruiz, M., Giudicelli, V., Foulquier, E., Truong, L., Thouvenin-Contet, V. and Lefranc G., IMGT unique numbering for immunoglobulin and T cell receptor variable domains and Ig superfamily V-like domains, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 27:55-77 (2003). PMID:12477501. |
| [13] | Lefranc, M.-P., Pommié, C., Kaas, Q., Duprat, E., Bosc, N., Guiraudou, D., Jean, C., Ruiz, M., Da Piedade, L., Rouard, M., Foulquier, E., Thouvenin, V. and Lefranc G., IMGT unique numbering for immunoglobulin and T cell receptor constant domains and Ig superfamily C-like domains, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 29:185-203 (2005). PMID:15572068. |
| [14] | Lefranc, M.-P., Duprat, E., Kaas, Q., Tranne, M., Thiriot, A. and Lefranc G., IMGT unique numbering for MHC groove G-DOMAIN and MHC superfamily MhcSF G-LIKE-DOMAIN, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 29:917-938 (2005). PMID:15936075. |